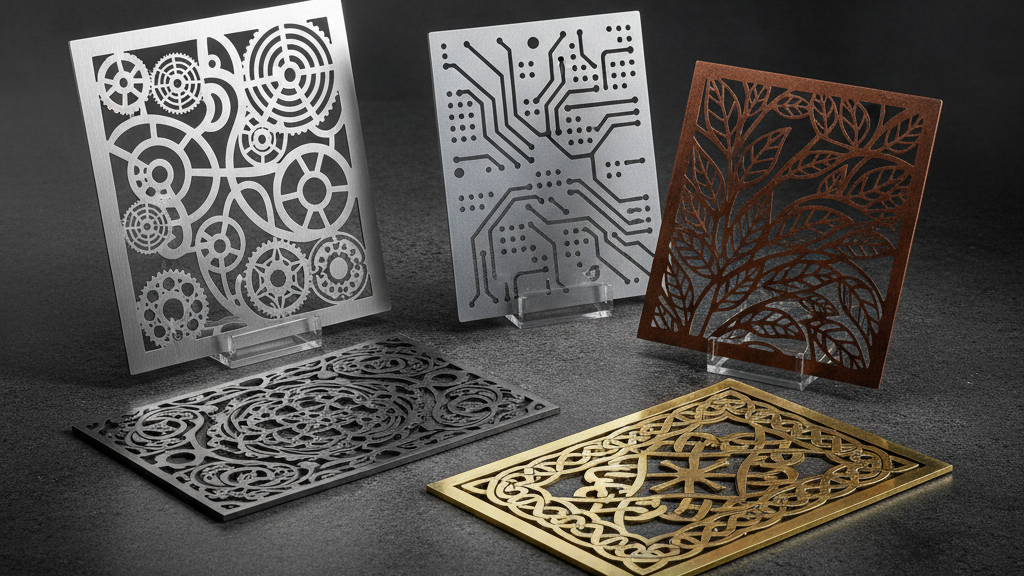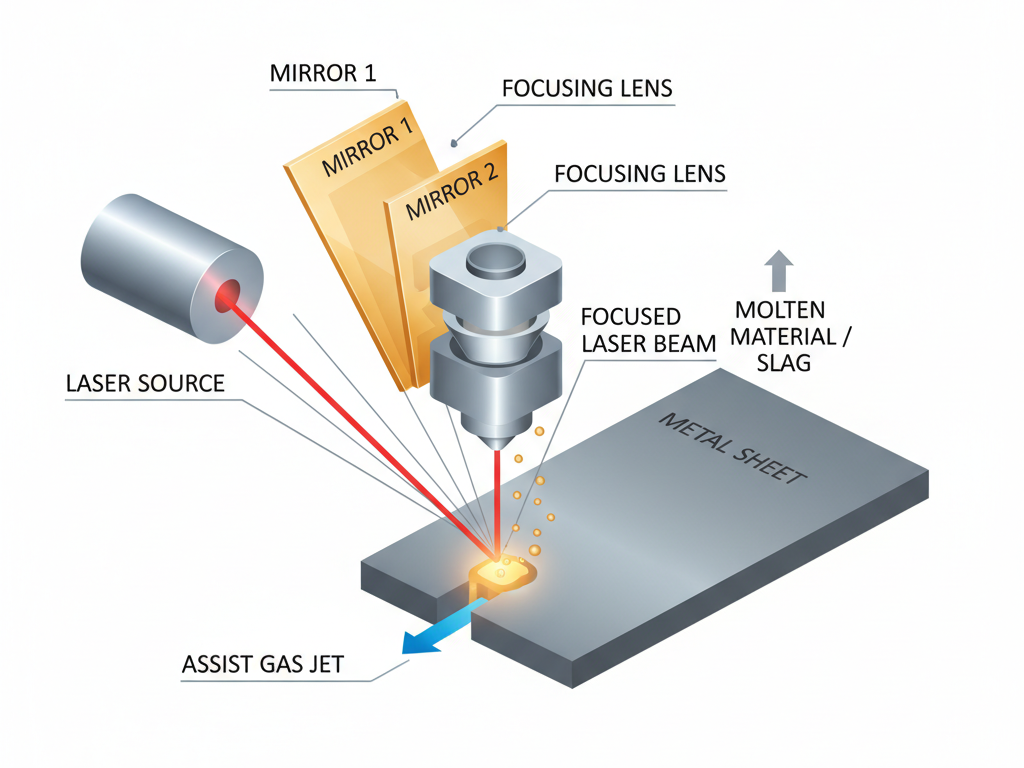
What Is Sheet Metal Laser Cutting?
- ±0.012 mm (±0.0005 inch)
- Kerf width as small as 0.15–0.3 mm
- Fiber laser power options ranging from 1 kW to 30 kW
The main types of laser sources include:
- Fiber Laser – Fast, energy-efficient, suitable for all metals
- CO₂ Laser – Suitable for non-metals and certain thin metals
- Nd:YAG Laser – Used for specialty manufacturing and highly reflective materials
With various equipment combinations, laser cutting can cover a wide range of applications—from ultra-thin sheets at 0.1 mm to thick plates over 30 mm.
Key Advantages of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting technology used by HorizonRP continues to see rapid growth across manufacturing industries in Europe, the United States, and Asia due to its outstanding technical capabilities.
1. Exceptional Precision and Consistency
- Accuracy: ±0.01–0.02 mm
- Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ): Extremely small, typically less than 0.3 mm
- Capable of producing complex curves, micro-holes, and lattice patterns
These characteristics make laser cutting ideal for:
- Aerospace
- Precision electronics
- Robotic joints and components
- Medical structural frames
2. High Speed and Outstanding Efficiency
Example with a 1500W laser source:
| Material | Thickness | Cutting Speed |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless steel | 1 mm | 35–45 m/min |
| Mild steel | 2 mm | 10–12 m/min |
| Aluminum alloy | 3 mm | 12–15 m/min |
With high-power systems (12–20 kW), speeds can reach:
- 1 mm stainless steel: > 80 m/min
- 6 mm carbon steel: 3–4×faster compared to mid-power systems
3. Low Cost and High Material Utilization
- Kerf width only 0.2–0.4 mm
- Automatic nesting increases material utilization by 15–20%
- Smooth edges with minimal post-processing required
This directly reduces material cost + labor cost + production cycle time.
4. Suitable for a Wide Range of Metals
Commonly processed materials include:
- Carbon steel
- Aluminum & aluminum alloys
- Stainless steel
- Copper / Brass
- Titanium

Laser Cutting vs Plasma Cutting vs Waterjet Cutting
In metal manufacturing and sheet metal fabrication, laser cutting, plasma cutting, waterjet cutting, and stamping are the four most widely used processes. Each cutting method differs significantly in precision, speed, cost, and application scenarios.
Based on HorizonRP’s long-term experience serving global customers, we found that for teams seeking sheet metal fabrication services, comparing laser cutting vs plasma cutting, or evaluating the global metal manufacturing supply chain, understanding these differences helps speed up decision-making and process selection.
Laser Cutting
It is ideal for thin to medium-thickness sheets, complex profiles, and high-standard products such as:
- Aerospace components
- Consumer electronics
- Robotic structural parts
Laser cutting is the best choice for multi-variety, small-batch, and short lead-time manufacturing.
Plasma Cutting
Best suited for fast processing of medium to thick metal plates, plasma cutting offers strong cost advantages.
Its drawbacks include higher edge roughness, more slag, and lower precision, making it unsuitable for precision components.
However, it is widely used in:
- Large steel structures
- Heavy machinery
- Industrial equipment fabrication
Waterjet Cutting
As a cold-cutting method, waterjet cutting produces virtually no heat-affected zone, making it compatible with metals, ceramics, glass, and composite materials.
It offers high precision but lower speed and higher cost, making it ideal for:
- High-value materials
- High-precision, small-batch projects
- Materials sensitive to heat
| Process | Precision | Cutting Thickness Range | Edge Quality | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Cutting | High (±0.02 mm) | 0.1–30 mm | Smooth, minimal post-processing required | Medium |
| Plasma Cutting | Medium–Low (±0.5 mm) | 6–50 mm+ | Rougher edges, requires grinding | Low |
| Waterjet Cutting | High (±0.05 mm) | 0–150 mm (any material) | Excellent, no heat effects | High |
Applications of Laser Cutting in Modern Manufacturing
Case 1 : New Energy Power Battery Components
A European–American new energy company required complex micro-channel structures for battery cooling plates. Traditional stamping could not achieve the required ±0.05 mm tolerance.
Horizon utilized a 3 kW fiber laser combined with CNC finishing to meet the stringent requirements:
- Micro-channel width: 0.8 mm
- Flatness: 0.03 mm
- Batch consistency: better than 99.5%
Case 2 : Robotic End-Effector Structural Components
A customer needed lightweight aluminum–magnesium alloy components with complex geometries and highly variable batch sizes.
By applying high-power fiber laser cutting, Horizon achieved:
- 28% reduction in unit manufacturing cost
- 40% reduction in delivery time
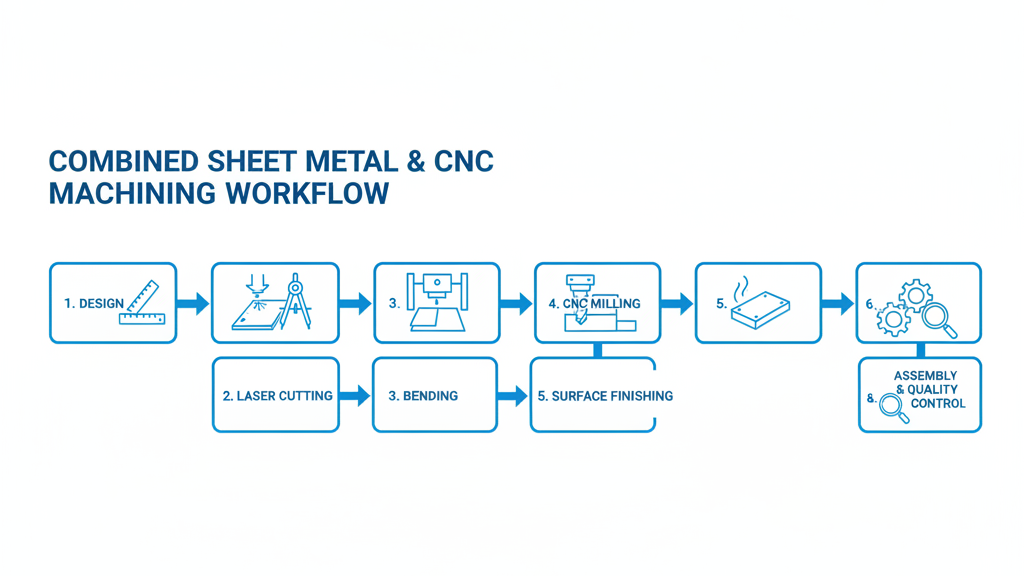
Combining CNC Machining with Laser Cutting
HorizonRP leverages laser cutting to solve key challenges such as rapid material preparation, complex contour cutting, and high-precision thin-sheet fabrication.
Meanwhile, CNC machining excels in:
-
High-precision surface machining
-
Deep holes, threads, and cavity features
-
±0.005 mm tolerance capability
When combined, the two processes create an extremely efficient and powerful integrated manufacturing workflow:
Laser Cutting + CNC Machining = The Optimal Solution for Precision Metal Parts
Process Comparison
| Process | Laser Cutting | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Best Use | Contour cutting, thin-sheet structures | Holes, steps, threads, precision functional surfaces |
| Advantages | Fast, low cost | Ultra-high precision |
| Materials | Sheet metals | All solid metal materials |
ypical Combined Use Case: Medical Device Housing
Laser cutting is used to produce:
- The outline of the housing
- Ventilation patterns and openings
CNC machining is applied to create:
- Threaded holes
- Mounting holes
- Precision locating surfaces
Final results:
- Appearance accuracy: ±0.03 mm
- Assembly precision: ±0.01 mm
- Delivery time: as fast as 48 hours
Industry Standards and Key Parameters
Common Industry Standards for Laser Cutting
- ISO 9013 – Quality classification for thermal cutting
- ISO 2768 – General tolerances for sheet metal parts
- EN 60825 – Safety standards for laser equipment
- AS9100 – Quality management system requirements for aerospace manufacturing
Key Parameter Selection Guide
| Parameter | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Fiber laser power | 1–6 kW (thin sheets), 6–20 kW (thick plates) |
| Cutting accuracy | ±0.02 mm |
| Surface roughness (Ra) | 1.6–3.2 μm |
| Minimum hole diameter | 1× material thickness |
Why Choose Horizon?
As a global leader in sheet metal fabrication and CNC machining services, Horizon provides customized manufacturing solutions for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics.
What we deliver for you:
- Fiber laser cutting precision: ±0.002 inch
- Kerf width: as narrow as 0.006 inch
- CNC machining precision: ±0.005 mm
- 24–72 hour expedited production
- Global logistics and engineering support
Top 3 Reasons Customers Choose Us
① Highly Skilled Engineering Team
We provide DfM (Design for Manufacturability) optimization to help reduce manufacturing costs by 10–30%.
② Strong Production Capacity
From one-off prototypes to 10,000-piece batches, we support fast and reliable delivery.
③ One-Stop Multi-Process Manufacturing
Laser cutting + bending + CNC machining + welding + surface finishing
No need to coordinate with multiple suppliers—lead times are reduced by 40%.
Submit Your Inquiry Now and Receive a Free Engineering Evaluation
If you are looking for:
- Higher-precision metal parts
- A more competitive and reliable supply chain
- Shorter lead-time manufacturing services
- An integrated Laser Cutting + CNC Machining solution
Horizon is the trusted partner you can count on.
📩 Contact us today to get a free quote and engineering analysis — we reply within 24 hours.
🌍 Website: https://www.horizrp.com