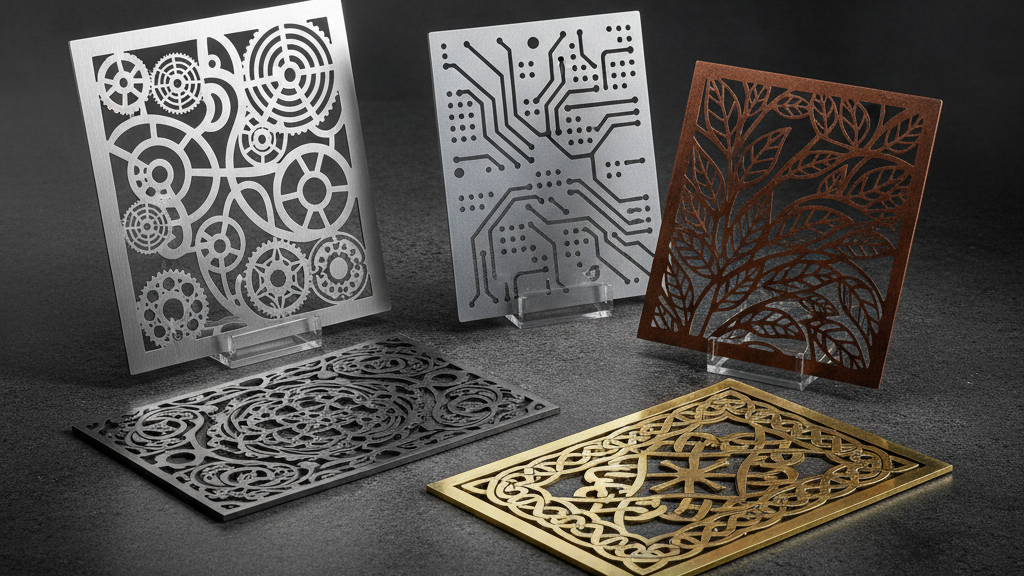
Metal products are everywhere—from automotive components and electronic devices to everyday items like metal railings, hardware decorations, and colorful hairpins. You might not be familiar with the term “surface treatment,” but when you see someone painting a metal railing at home, you’re actually witnessing one of the most common forms of metal surface treatment. Metal surface treatment is a crucial process that enhances both the performance and appearance of metal: without it, even the strongest metals can corrode, wear out, or fail to meet functional and aesthetic requirements.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to metal surface treatment, covering its importance, common techniques, key benefits, and applications across industries, while also highlighting potential issues in the process. It will help you gain a more systematic understanding of this essential manufacturing technology.
What Is Metal Surface Treatment?
Metal surface treatment refers to a series of mechanical, physical, or chemical processes that modify the surface of metal components. These treatments enhance durability, corrosion resistance, aesthetics, and functional performance.
The role of surface treatment:
- Improve hardness and wear resistance
- Prevent corrosion and oxidation
- Enhance appearance and surface texture
- Increase coating adhesion
- Improve electrical and thermal performance
Common Metal Surface Treatment Techniques
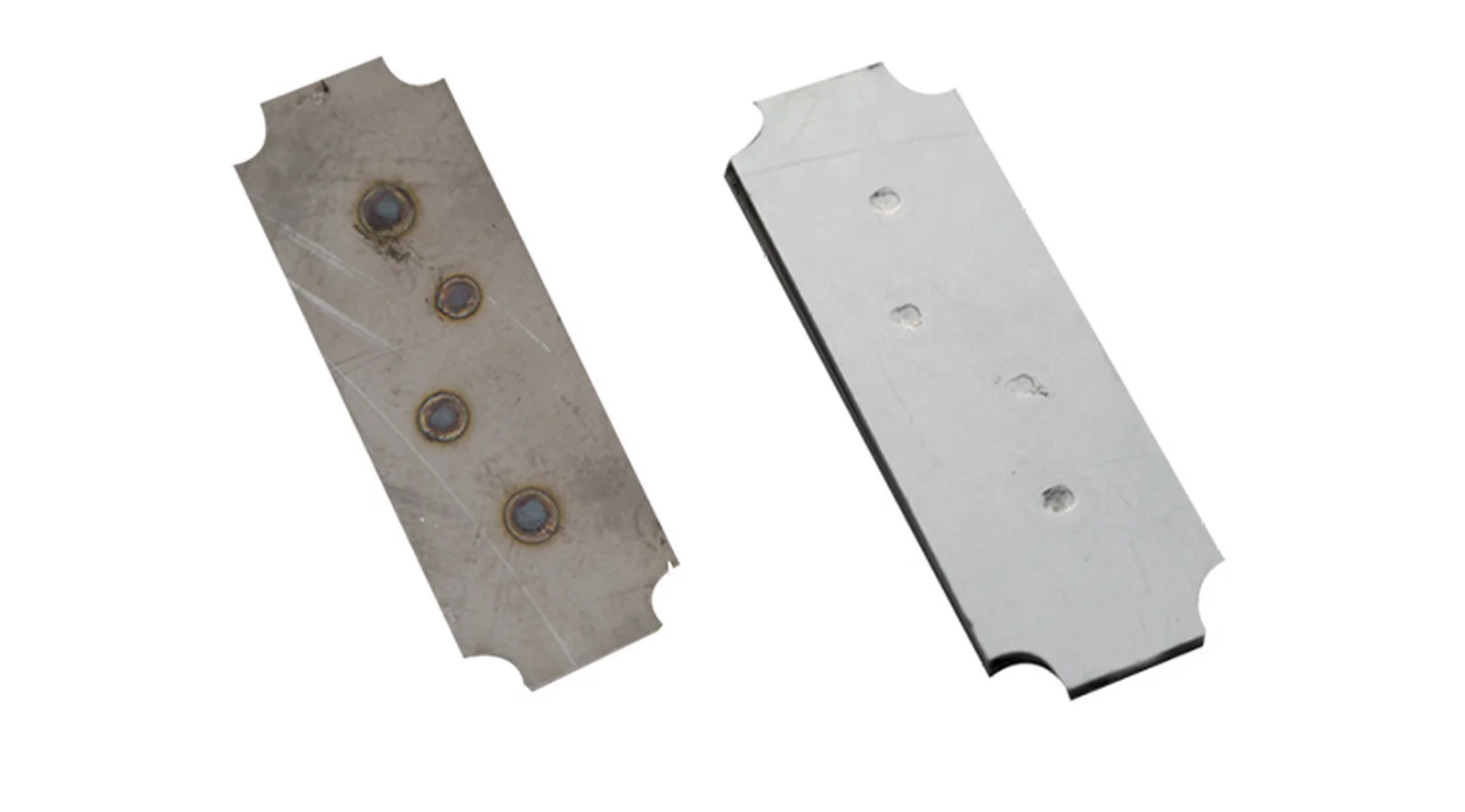

Different projects require different finishing methods. Below are widely used processes in modern manufacturing.
Mechanical Polishing
This involves using abrasives or sandpaper to remove surface scratches or improve surface smoothness and appearance. Common techniques include vibratory polishing, buffing, brushing, and sandblasting.
Chemical Treatment
Chemical methods use chemical agents to remove impurities from the metal surface and form a protective layer through chemical reactions. Examples include pickling, phosphating, and chemical plating (such as electroless nickel or silver plating).
Surface Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is a process that changes the internal structure of metals or alloys through heating, holding, and cooling, thereby improving mechanical properties, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. Common heat treatment methods include annealing, tempering, carburizing, and nitriding.
Coating (Spray) Treatment
This involves uniformly spraying coatings onto the metal surface. It not only enhances corrosion resistance and improves appearance but also increases the product’s overall value.
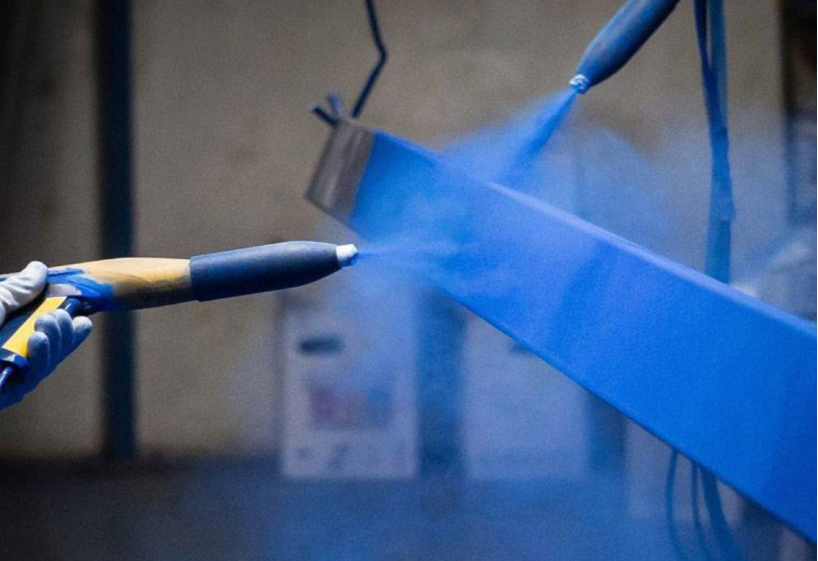
How Surface Treatment Improves Metal Performance
Different treatments produce different functional benefits. Below are key improvements:
Corrosion Resistance
Electroplating, anodizing, and coatings create a barrier that prevents moisture and oxygen from contacting the metal.
Wear Resistance
Hard coatings and heat treatment improve durability in gears, shafts, and high-friction components.
Enhanced Appearance
Polishing, painting, and powder coating offer smooth textures, bright finishes, and decorative colors.
Improved Coating Adhesion
Processes like phosphating and sandblasting prepare surfaces for better paint or plating adhesion.
Reduced Friction
Grinding and polishing lower resistance, improving mechanical efficiency and lifespan.
Common Surface Treatment Defects and Solutions
Even with precise processes, defects may occur. Proper quality control ensures consistent results.
| Defect | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scratches (anodizing) | Improper handling | Train operators, reduce force, handle gently |
| Surface bubbles (electroplating) | Incomplete cleaning | Improve pre-cleaning and degreasing |
| Peeling / poor adhesion | Low surface roughness | Sandblasting, phosphating, better pretreatment |
| Discoloration / corrosion | Chemical residue | Enhance rinsing and control solution parameters |
Industry Applications of Surface Treatment
Metal finishing is used across many major industries:
Aerospace
High-performance coatings improve reliability under extreme conditions.
Automotive
Chrome plating and painting provide durability and visual appeal.
Medical Devices
Passivation improves stainless steel biocompatibility.
Consumer Electronics
Gold, silver, and nickel plating improve conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Industry Standards for Surface Treatment
Surface finishing follows strict global standards to ensure safety and quality.
- Anodizing: ISO 7599, ASTM B580, MIL-A-8625
- Electroplating: ISO 6158, ASTM B456, MIL-STD-171
- Passivation: ASTM A967, MIL-DTL-5541
Limitations of Surface Treatment
While beneficial, finishing processes may have challenges:
- Higher production costs
- Material compatibility issues
- Environmental hazards (chemical waste)
- Difficulties maintaining coating uniformity
- Potential dimensional changes during heat treatment
Partner With Horizon for High-Quality Surface Finishing
At Horizon, we specialize in precision metal machining and finishing. Our ISO 9001:2015–certified processes ensure consistent quality. We offer:
- Anodizing
- Powder coating
- Electroless plating
- Polishing & grinding
- Custom finishing solutions
Whether you need prototypes or mass-production finishing, our team provides reliable, high-performance surface treatments to meet your project requirements.
Contact us anytime for professional support and quotes.