1.Fast Lead Time
Leveraging certified domestic factories and an integrated supply chain, we shorten your product development timeline and deliver overmolded parts quickly—without compromising quality.
2.High Quality Parts
Backed by certified factories and strict quality control—including in-process inspections and dimensional checks—we guarantee consistent accuracy and reliability for even the most complex custom-molded parts.
3.Engineering Support
With a team of injection molding specialists boasting 10+ years of experience, we streamline the transition from prototype to production, ensuring fast, reliable, and optimized results.
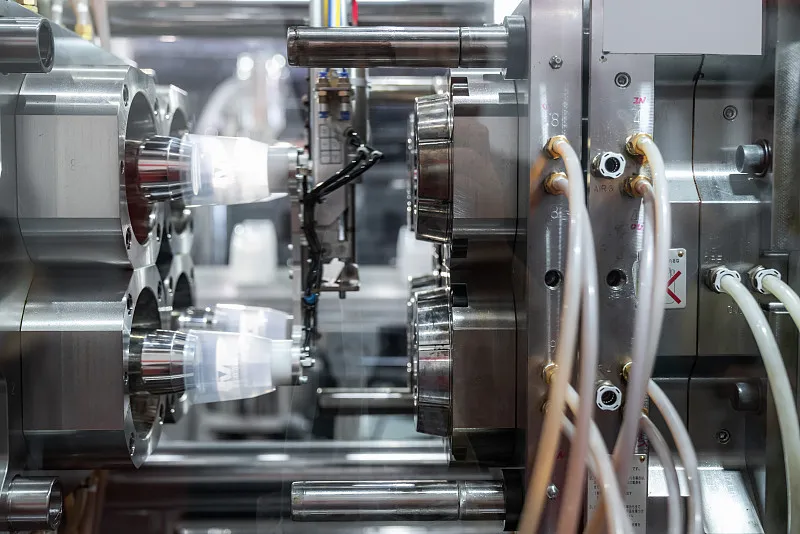
What is Insert Molding?
Insert molding is a manufacturing process where metal or other components are placed into a mold, and plastic is molded around them to create a single, unified part. This process improves strength, precision, and durability, while enabling complex assemblies in a wide range of products—from electronics and automotive parts to medical devices and consumer goods.
Advantages of Insert Molding
- Enhanced Strength & Durability – Embeds metal or functional inserts for superior mechanical performance.
- Precision & Reliability – Ensures tight tolerances and consistent part quality.
- Cost Efficiency – Reduces assembly steps, adhesives, and fasteners.
- Design Flexibility – Combines multiple materials and components in one process for innovative product solutions.

How to Work With Us
Upload a CAD File
To start, simply select a manufacturing process and upload a 3D CAD file.
Get Quote with DFM
Within a few hours we’ll send you design for manufacturability(DFM) analysis andreal-time pricing.
Manufacturing Begins
Once you review your quote and place your order, we’ll start the manufacturing process. We also offer finishing options.
Parts are Shipped!
Our digital manufacturing process allowsus to produce parts in as fast as 1 day.
Insert Molding Materials
PC+ABS
PC/ABS (Polycarbonate‑ABS Blend) Plastic Material PC+ABS is a blend-modified material that combines the advantages of both materials. It not only inherits the high impact resistance of PC but also the material strength of ABS, while improving its heat resistance. It is often used in electronic product casings, automotive interiors, consumer products, and more.
CPVC
CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) Plastic Material CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) is a modified form of PVC, with enhanced thermal stability, mechanical properties, and chemical resistance. These upgraded characteristics make CPVC an excellent choice for applications in high-temperature and corrosive environments where ordinary PVC would fail.
PC+GF
PC+GF(Glass‑Fiber Reinforced Polycarbonate) Material PC+GF (polycarbonate + glass fiber reinforced composite material) is a reinforced engineering plastic made by adding glass fiber (abbreviated as GF) to a polycarbonate (PC) matrix. The addition of glass fiber can significantly improve the mechanical properties and stability of pure PC while retaining some of PC’s excellent inherent properties, making
PEI
PEI (Polyetherimide) Engineering Material PEI (polyetherimide) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for excellent heat resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical stability. It is widely used in demanding applications across aerospace, electronics, medical, and industrial fields.
PTFE
PTFE Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, is a high-performance fluoropolymer. It is frequently used in mechanical components requiring reduced friction and wear—such as bearings, gears, and piston rings—due to its non-stick properties, low friction characteristics, and self-lubricating capabilities. PTFE also exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties, making it highly suitable for applications like high-frequency cables,
LDPE
LDPE Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is lighter than water, soft and tough, with excellent acid and alkali resistance as well as electrical insulation properties. It is widely used in fields such as packaging, agriculture, electronics, and daily necessities.
PP
PP Polypropylene (PP) is a well-balanced thermoplastic characterized by lightweight material, excellent chemical resistance, and good flexibility. Owing to these properties, it finds wide application in fields such as packaging, household appliances, automotive, daily necessities, and medical devices.
PET
PET PET (polyethylene terephthalate) is a common thermoplastic polyester with excellent mechanical properties and strong chemical resistance. It also offers glass-like transparency and luster, with a high light transmittance of about 88–92%, and is widely used in beverage bottles, food packaging, and engineering plastics.
PVC
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Plastic Material Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer material characterized by excellent mechanical properties, outstanding corrosion resistance, and superior electrical insulation performance. By incorporating various additives, it can be tailored to meet customized requirements. Owing to its unique combination of properties, PVC finds extensive applications in fields such as
PC
PC (Polycarbonate) Engineering Material PC (polycarbonate) is a versatile engineering plastic known for its high impact resistance, optical transparency, and good thermal stability. It combines toughness, heat resistance, and aesthetic clarity, making it suitable for a wide array of applications.
PMMA (Acrylic)
PMMA (Acrylic) Engineering Material Acrylic (also known as polymethyl methacrylate, PMMA) boasts not only excellent optical performance but also outstanding UV resistance. With a light transmittance of up to 92%—comparable to glass—it has become a popular material in scenarios ranging from neon signs in shopping malls and display case panels in museums to precision optical
PEEK
PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) Engineering Material PEEK (polyetheretherketone) is a premium thermoplastic widely recognized for its exceptional thermal stability, mechanical strength, chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and in many cases biocompatibility and electrical insulation. It is used in extreme environments like aerospace, medical implants, electronics, and semiconductor industries.
Nylon
Nylon (Polyamide) Engineering Material Nylon (polyamide) is a versatile engineering thermoplastic known for its high strength, excellent wear resistance, good chemical stability, and toughness. It is widely used across industries for gears, bearings, bushings, automotive components, industrial parts, and more. Its ease of machining, coupled with its chemical resistance, also makes it suitable for applications
POM
POM (Polyoxymethylene / Acetal) Engineering Material POM (polyoxymethylene), also known as acetal, is a high‑performance engineering thermoplastic valued for its rigidity, low friction, excellent wear resistance, and good dimensional stability. It is often used in precision mechanical parts that require durable, low‑maintenance performance.
HIPS
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) Material HIPS, or High Impact Polystyrene, is a modified polystyrene polymer enhanced with rubber modifiers (usually polybutadiene) to improve toughness and durability. The result is a rigid yet impact-resistant thermoplastic that retains good processability, making it popular in prototyping, manufacturing, and consumer products. HIPS combines the stiffness of polystyrene with improved
HDPE
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) Material High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with high strength-to-density ratio, known for durability, chemical resistance, and ease of processing. As a semi-crystalline plastic, it offers excellent impact performance, low moisture uptake, and good machinability — making it a popular choice in industrial, chemical, packaging, and structural applications. It is great
ABS
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) Material ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a widely used engineering thermoplastic known for its excellent balance of strength, toughness, and processability. Because it combines rigidity from acrylonitrile and styrene with impact resistance from butadiene, ABS is commonly used in consumer products, enclosures, housings, and structural components.
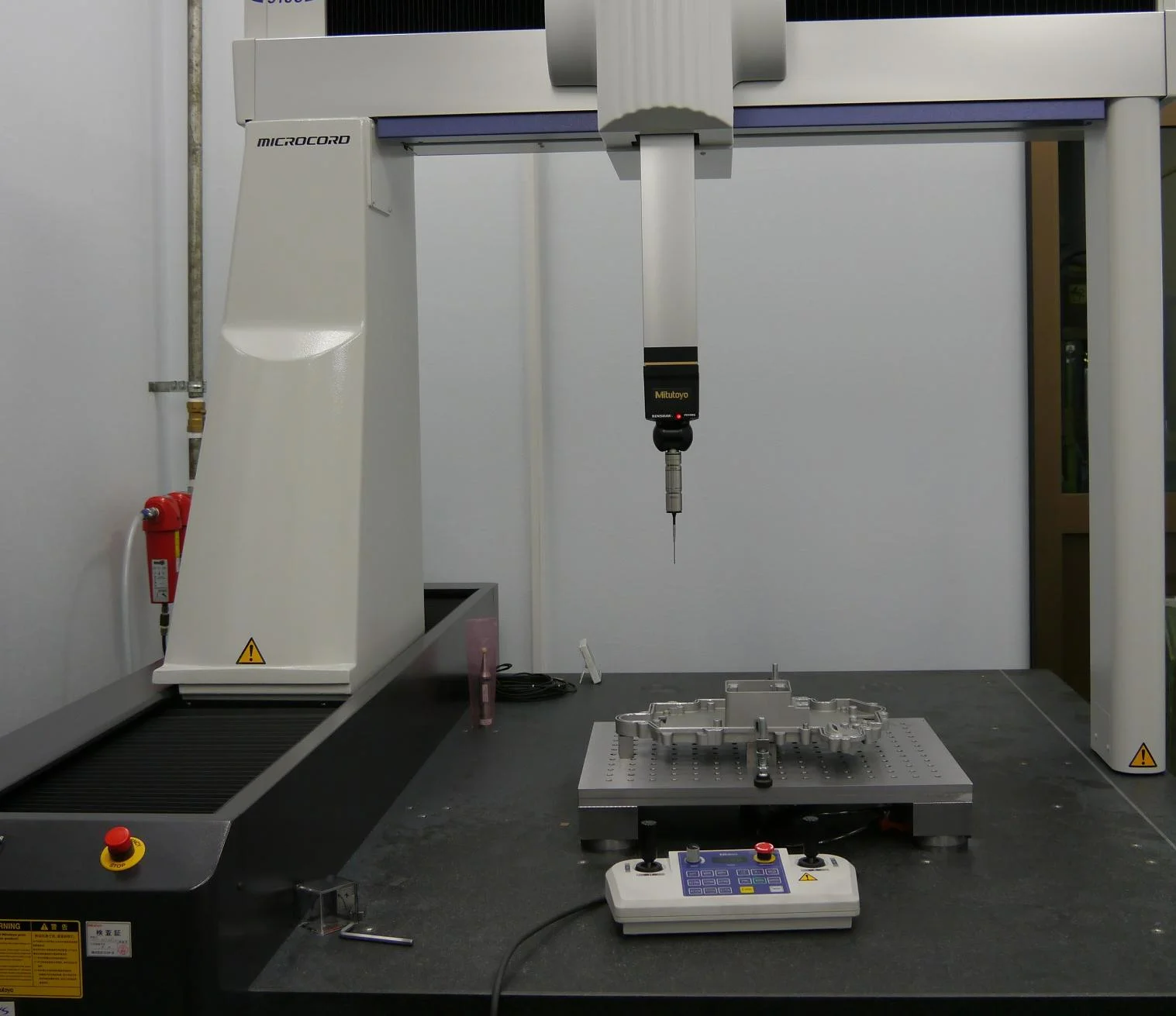
Quality Assurance
| Driven by excellence, we embed quality into every detail—from advanced tools to rigorous standards. We ensure consistent, outstanding quality. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
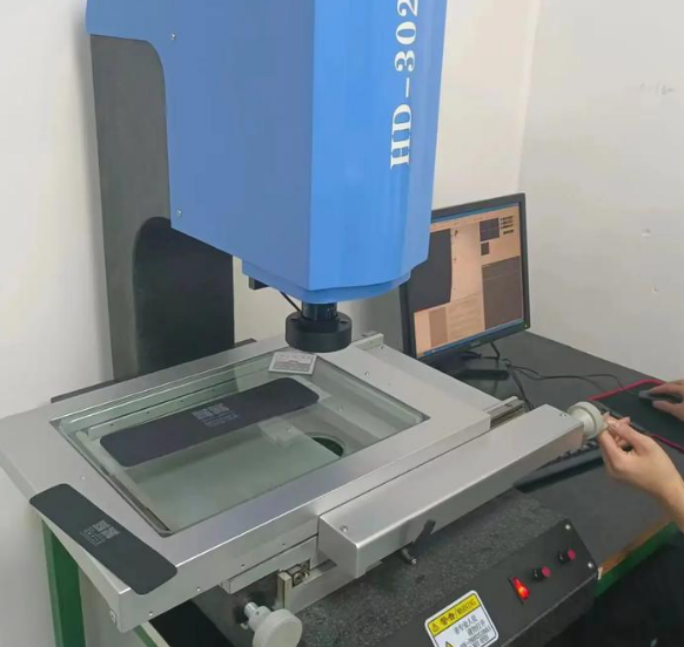
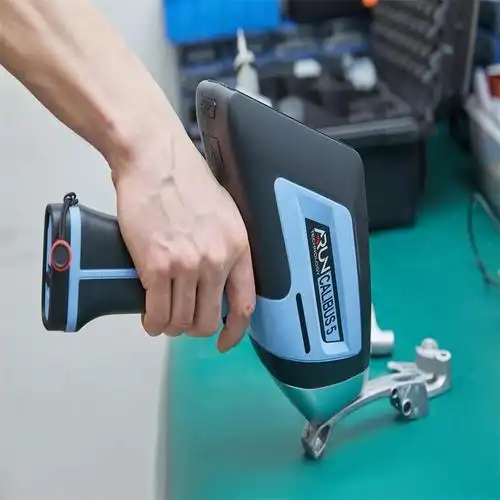
| 1 | Advanced Inspection Equipment | ||||
| We employ professional inspection equipment for precise measurement and validation. A spectrometer analyzes metal composition, a 2.5D measuring instrument verifies detailed features, a coordinate measuring machine (CMM) inspects complex three-dimensional structures, and height gauges ensure the accuracy of fundamental dimensions. | |||||
| 2 | Strict quality management system | ||||
| From first article inspection to in-process checks and final pre-shipment testing, every stage is governed by a rigorous management system to ensure consistent quality. | |||||
| IQC(Incoming Quality Control) | FAI (First Article Inspection) | ||||
| IPQC(In-Process Quality Control) | CMM inspection report | ||||
| FQC(Final Quality Control) | DIR(Dimensional Inspection Report ) | ||||
| OQC(Outgoing Quality Control) | CAR(Corrective and Preventive Action Report) | ||||
| Material Certificates | ISO 9001 | ||||
Expanded injection molding capabilities
Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten plastic is injected into a mold under high pressure, then cooled to form the desired part. It precisely reproduces complex designs and is widely used in consumer electronics, automotive components, medical devices, and more.
Overmolding
Overmolding is a manufacturing process where one material is molded over or around another, creating a single seamless part. It enhances functionality, comfort, and durability, while allowing multi-material designs in a wide range of products—from grips and handles to medical devices and automotive components.
Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Molding is a manufacturing process where liquid silicone is injected into a heated mold, then cured to form flexible, durable, and high-precision parts. It enables the production of complex geometries with excellent biocompatibility, heat resistance, and electrical insulation. LSR molding is widely used in medical devices, automotive components, consumer products, and electronic applications.