Innovative Companies We Support





Types of Precision Machining That We Offer
We provide custom 3D printing (additive manufacturing) services with four advanced 3D printing technologies, efficiently turning your 3D files into finished parts made of plastics, metals, and more. Using FDM, SLA, SLS, and SLM processes, we offer a wide range of options for both prototyping and production.
3D printing is the ideal method for creating one-off parts or small-batch products. With our outstanding production capacity, we can deliver parts in as fast as 2 days. In addition to a broad selection of materials, we also provide comprehensive post-processing solutions to enhance both the appearance and mechanical performance of parts, ensuring they are both aesthetically pleasing and structurally strong.
SLA
Stereolithography (SLA) technology uses an ultraviolet laser to cure liquid photosensitive resin layer by layer, stacking them until a complete part is formed. It produces smooth surfaces with fine detail, making it ideal for creating prototypes and complex designs that require high precision and excellent appearance.

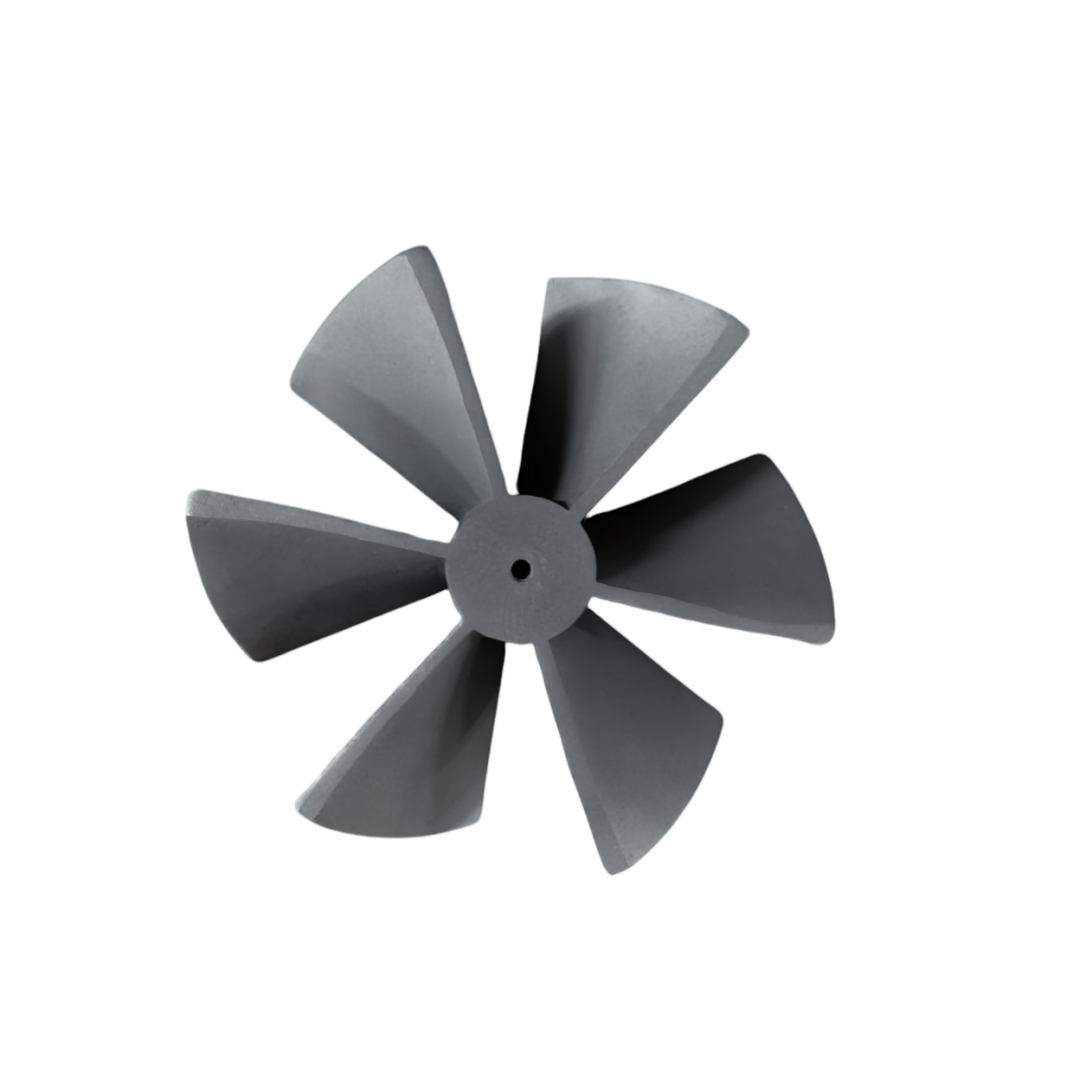
SLS
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) uses a high-power laser to melt and solidify polymer powder particles layer by layer, ultimately forming strong and durable parts. SLS-printed components exhibit excellent mechanical properties, making the technology highly suitable for manufacturing functional parts with complex geometries.

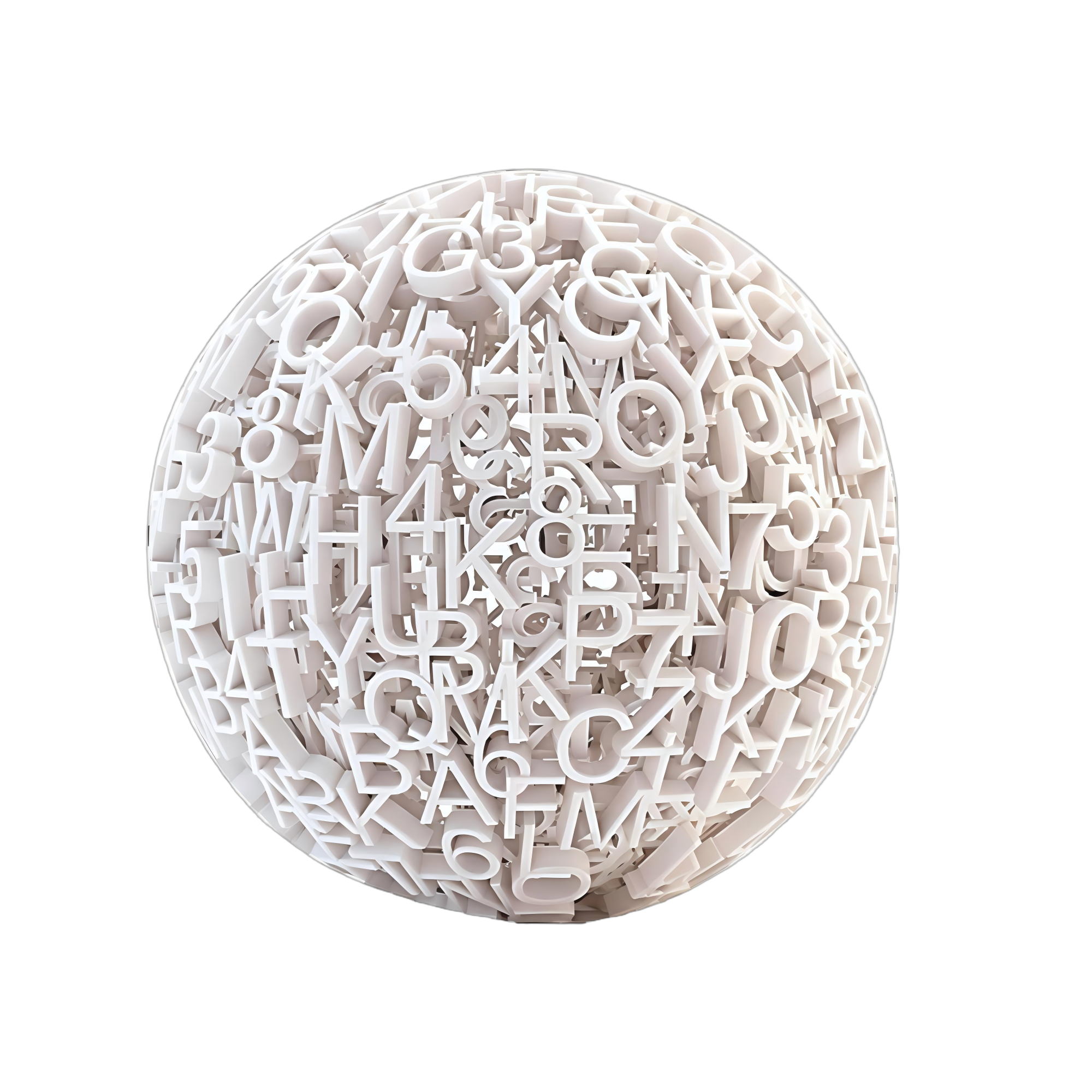
FDM
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a technology that builds solid parts by heating and extruding thermoplastic filament, which is then deposited layer by layer. Compared with SLS, it offers lower costs. FDM is well-suited for cost-sensitive projects, rapid prototype validation, or parts requiring high material toughness, and is commonly used in educational models and medical assistive devices.
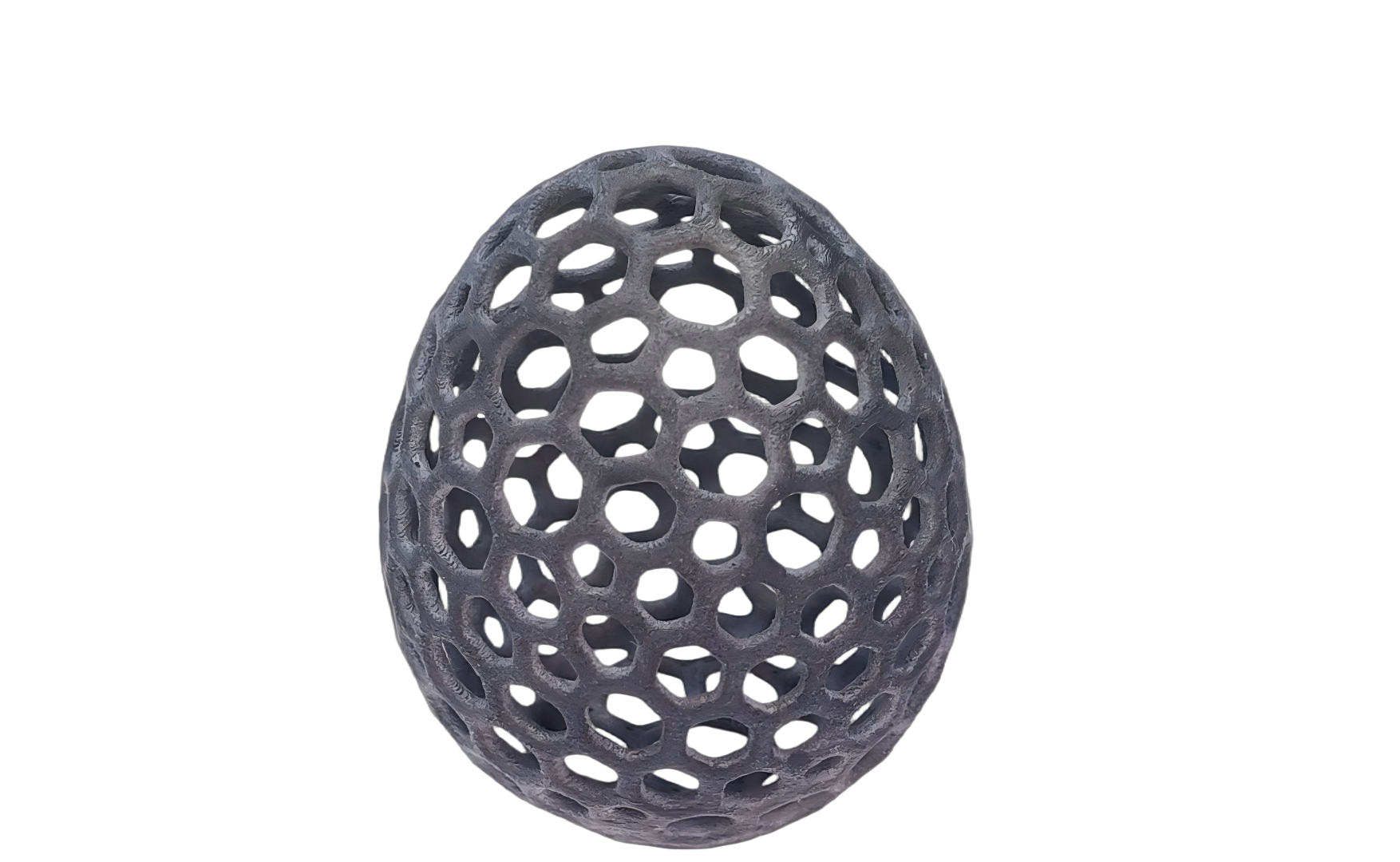
SLM
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is an additive manufacturing technology that directly produces metal parts from metal powders. The process uses a high-energy laser beam to selectively melt and fully fuse the metal powder layer by layer, ultimately forming dense and high-strength metal components. SLM is particularly suitable for producing complex geometries and functional metal parts with high mechanical performance requirements.
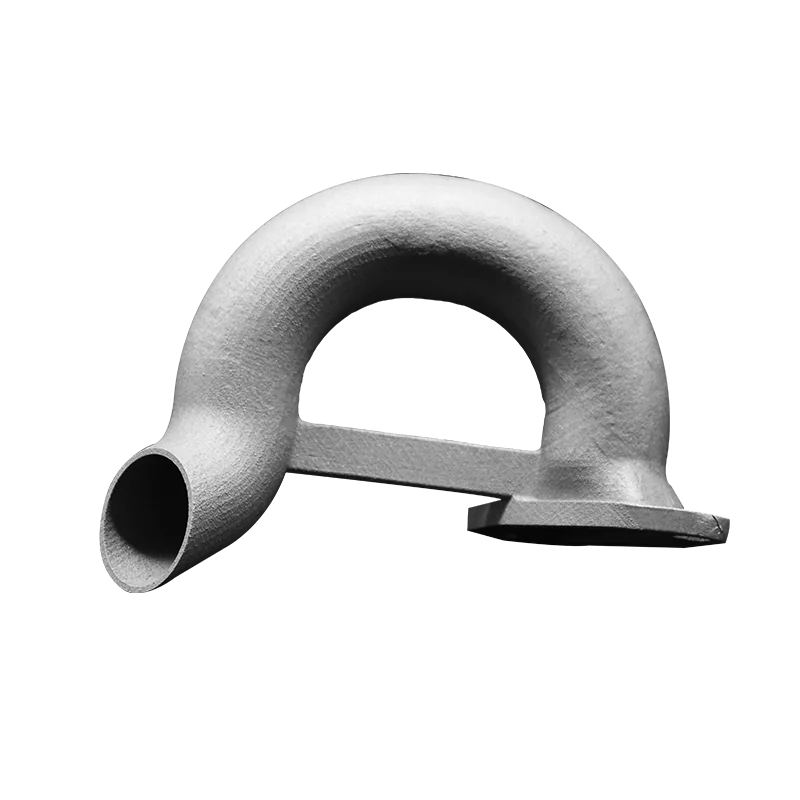

MJF
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is an additive manufacturing technology that directly produces metal parts from metal powders. The process uses a high-energy laser beam to selectively melt and fully fuse the metal powder layer by layer, ultimately forming dense and high-strength metal components. SLM is particularly suitable for producing complex geometries and functional metal parts with high mechanical performance requirements.
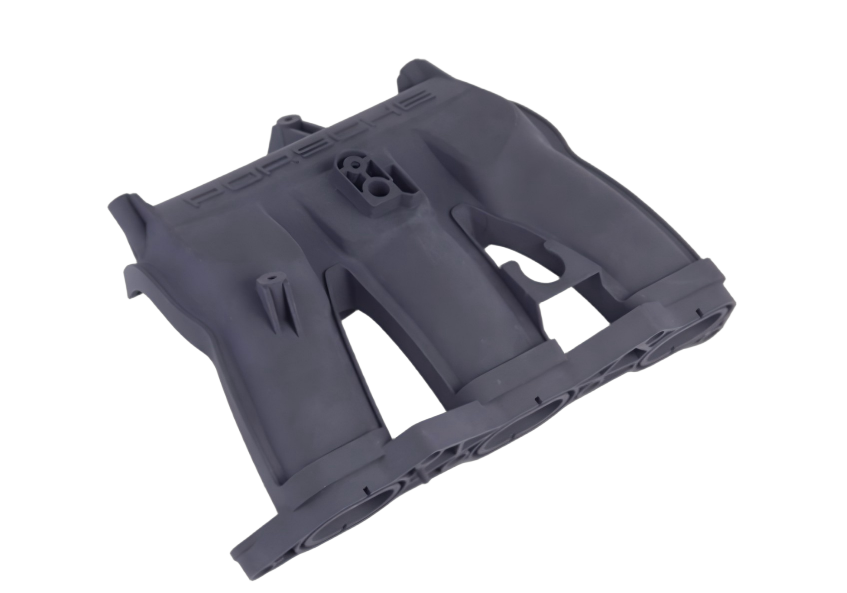

Compare 3D Printing Processes
First time using our 3D printing service and still unsure which additive technology best fits your 3D design? Feel free to check out the performance comparison of each process below to easily find the solution that best matches your application needs.
| Technology | Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLA | Photosensitive resin (general / heat-resistant / tough) | High precision, smooth surface, rich in detail | Brittle material, must be kept away from light, post-processing requires curing |
| SLS | PA, TPU, PA+GF, PA+CF | Excellent mechanical properties, can produce complex structural parts | Grainy surface, high cost |
| FDM | PLA, ABS, PETG | Low cost | Low precision, relatively rough surface |
| SLM | TC4, Aluminium, Stainless steel (316, 17-4 PH), Inconel | Excellent mechanical properties, can produce complex structural parts | Slight surface pits and layer texture, high cost |
| MJF | PA | Excellent mechanical properties, can produce complex structural parts, surface quality better than SLS | Limited material options |
3D Printing Materials
plastic 3D Printing Materials

 ABS is an engineering plastic that combines strength, durability, and machinability. With a smooth surface finish and excellent impact resistance, it is the ideal choice for functional prototypes and mechanical parts.
ABS is an engineering plastic that combines strength, durability, and machinability. With a smooth surface finish and excellent impact resistance, it is the ideal choice for functional prototypes and mechanical parts.

Resin is a liquid photopolymer plastic used in 3D printing, ideal for high-detail prototypes with smooth surfaces and fine features. The common subtypes include Resin 8119, 8118H, 8228, and 8338.

TPU are flexible materials that can be used for FDM. It is a highly elastic material with high tear and abrasion resistance, as well as satisfactory thermal resistance.

PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic used in FDM, offering ease of printing, good surface finish, and low warping—ideal for prototypes and models.

Polycarbonate (PC) can be used for FDM, combining excellent strength and heat resistance—perfect for tooling, fixtures, and load-bearing parts.
Metal 3D Printing Materials
3D-printed aluminum alloy parts offer excellent strength and heat resistance, with higher strength compared to traditional casting. They also support processing techniques such as anodizing, polishing, and shot peening.
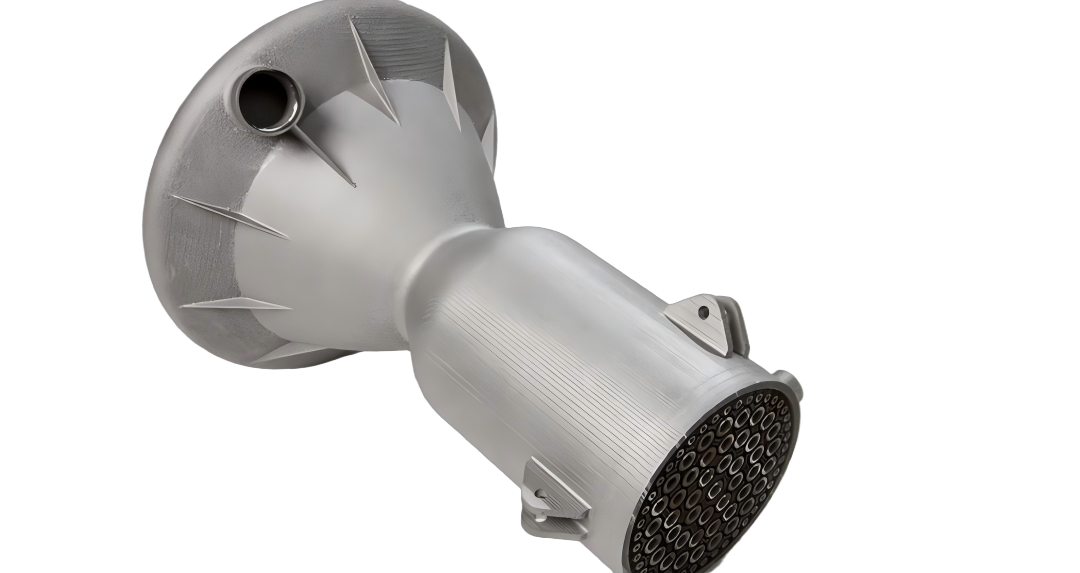

3D-printed stainless steel parts feature excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and high hardness, while supporting post-processing techniques such as passivation, polishing, and shot peening. We offer two material options:
-Stainless Steel 316L
-Stainless Steel 17-4 PH
Titanium, as a lightweight alloy, combines high strength, corrosion resistance, and excellent biocompatibility, and is widely used in aerospace, medical and other fields.
Nickel alloys are a material with high strength, high temperature resistance and excellent corrosion resistance. They perform exceptionally well in high-temperature corrosive environments and are often used in manufacturing turbines and components for extreme temperature environments.
3D printing post-processing solutions
Looking to boost the strength, clarity, or appearance of your 3D-printed parts? Choose from microfluidic and micro-resolution materials, metal plating, secondary machining, and custom finishes like painting, clear coating, and decaling.
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Clear Coat | Clear cosmetic finish that can be applied to ABS-Like Translucent/Clear and PC-Like Translucent/Clear materials. |
| Painting | After smoothing the part with sanding and polishing,parts can be painted with automotive-grade paint. Provide a pantone color with your quote request.We also offer soft-touch painting. |
| Plating | Electroless nickel plating can be used to achieve parts that are similar to cast aluminum or magnesium. |
| Dyeing | Dyeing is another method for adding color to 3D prints. This is faster option with alimited color selection, so is a more cost-effective choice than painting. |
| Decaling | Decaling can be used to add a logo or other graphics to boost cosmetics or function. |
| Polishing | We can polish parts to a miror-like finish.If this is a requirement,we ask that you provide either a drawing or image that indicates your finish expectations. |
| Heat Treatment | Harden and strengthen metal 3Dprints with multiple heat treatment options: NADCAP heat treatment, hot isostatic pressing (HIP), solution annealing,and aging. |
| Machining | Machine metal 3D prints to achieve exceptional surface finish quality or meet tight tolerances. |
What are Horizon’s custom 3D printing Services?
Exceptional Quality
Our experienced engineering team provides professional design reviews for every project and tailors the optimal solution based on your specific application needs.
Diverse Materials
We offer a full range of options, from high-performance thermosetting resins and thermoplastics to metal powders. Combined with post-processing techniques such as secondary machining, anodizing, and polishing, we enhance both mechanical performance and visual appeal, adding quality and competitiveness to your products.
Rapid Delivery
With 24/7 production, we can quickly respond to urgent orders, whether for small-scale prototypes or large-scale production. Delivery can be completed in as fast as 24 hours.
Choose Us
High quality, diverse materials, and fast delivery — ensuring a seamless transition from design to finished product, keeping you one step ahead in the market.

Horizon’s 3D Printing Capabilities ?
We provide a comprehensive overview of each 3D printing process’s unique standards, aiding in informed decisions for your printing needs.
| Parameters/Processes | FDM | SLA | SLS | SLM | MJF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. Build Size | 1000x610x610 mm | 2100x1000x700 mm | 550x550x850 mm | 427x460x527 mm | 277x377x380 mm |
| Min. Wall Thickness | 0.8 – 1.2 mm | 0.4 – 0.6 mm | 0.7-1.0 mm | 0.8-1.5 mm | ~1mm |
| Layer Thickness | 0.05-0.4 mm | 0.025-0.1mm | 0.1-0.12mm | 0.03-0.05mm | ~0.08 mm |
| Design Tolerance | ±0.2 ~ ±0.5 mm | ±0.05 ~ ±0.1 mm | ±0.2-±0.3mm | ±0.2mm | ±0.3mm |
| Standard Lead Time | 5 days | 5 days | 6 business days | 6 business days | 7 business days |
| Note: Excluding rest days. Delivery time varies with the order quantity, and is specifically subject to the actual order quantity. | |||||

What’s 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a cutting-edge technology driving innovation in the manufacturing industry. It precisely builds three-dimensional objects from digital models by layering materials until the final product is formed, in stark contrast to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods. This technology enables companies to achieve highly complex geometries and precise details with minimal material waste. 3D printing delivers exceptional value across prototyping, product development, medical implants, aerospace components, and more, significantly enhancing customization, production efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. As a key driver of modern manufacturing, 3D printing empowers businesses to accelerate innovation and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Advantages of 3D Printing
3D printing offers multiple advantages over traditional manufacturing methods:
Applications of 3D Printing
The applications of 3D printing are extensive, spanning multiple industries from prototype development to end-use products:
Explore 3D Printing Resources

What is 3D printing?
Gain an understanding of additive manufacturing and explore the applications of 3D printing in rapid prototyping and production to shorten the product development cycle.
3D Printing Materials
Understand the properties of plastic and metal 3D printing materials to make your products better, development more efficient, and costs lower.

3D Printing Design Errors & Fixes
3D printing design errors, like thin walls or weak supports, can cause failures and affect quality. Learn how to spot and fix them to make your prints more reliable and outstanding!



