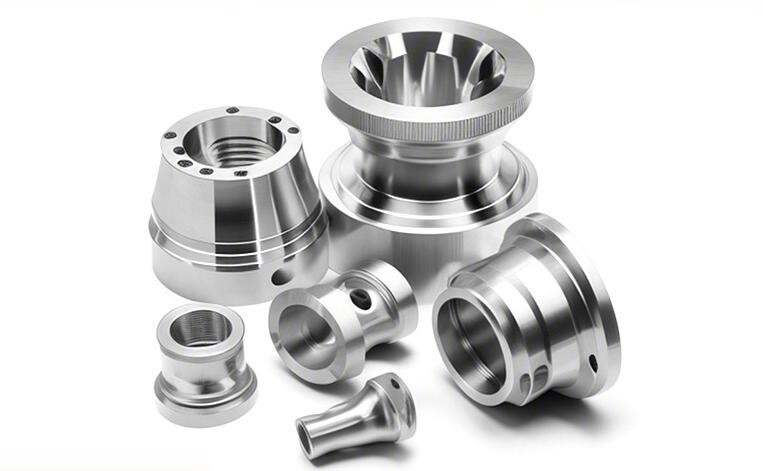
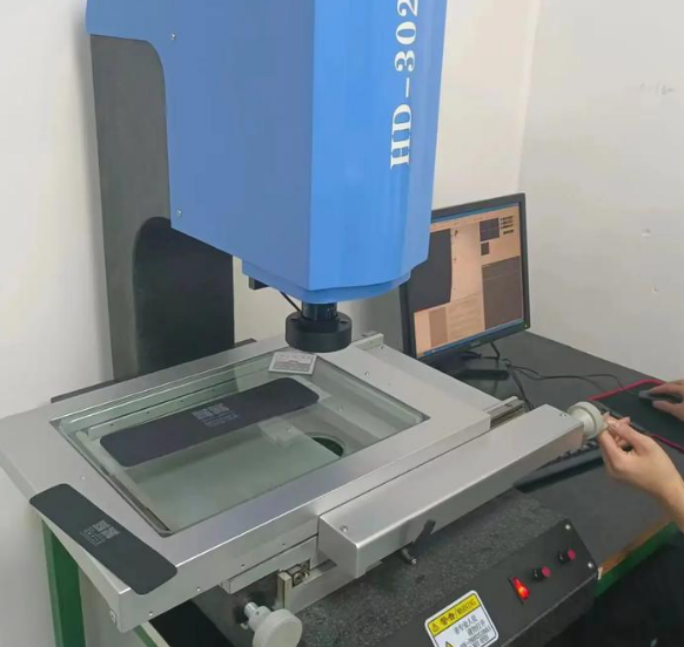
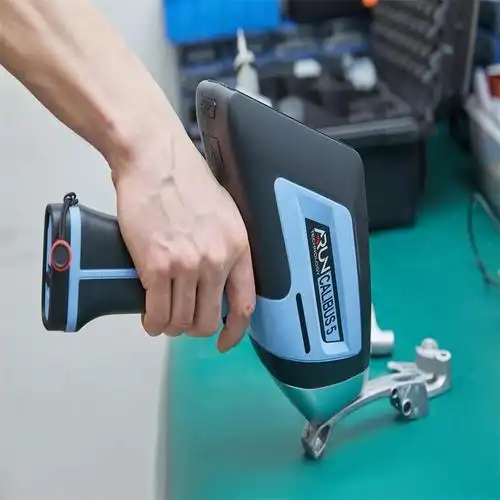
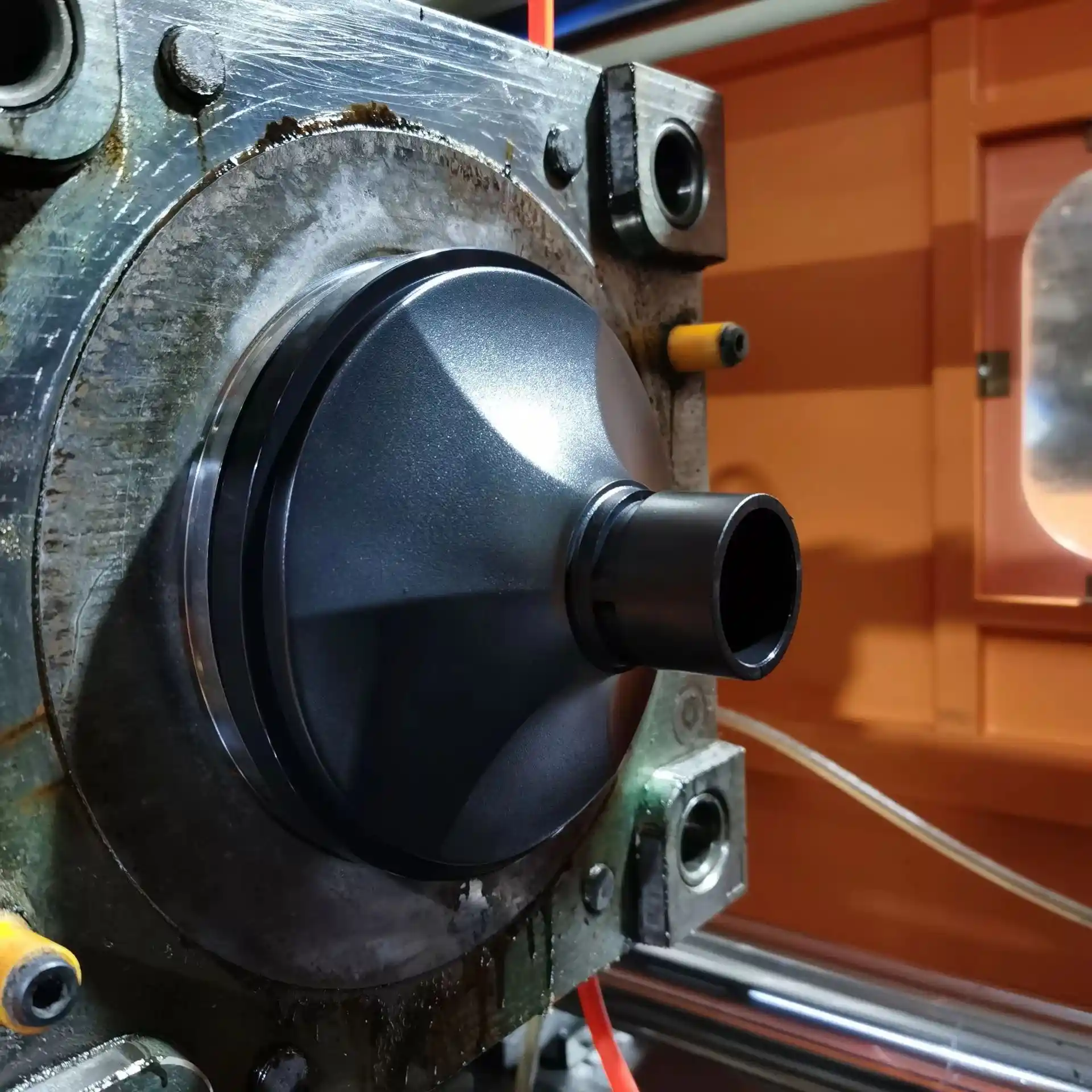
PROTOTYPING & MANUFACTURING
Low-Volume Manufacturing Service
When you need production quantities that fall between prototyping and full-scale mass production, low-volume manufacturing offers the ideal solution. It allows you to get high-quality, end-use parts in quantities ranging from a few hundred to tens of thousands—quickly and cost-effectively—while keeping flexibility for design adjustments and faster time to market.
If you’re still at an earlier stage of product development, we also provide a comprehensive Rapid Prototyping Service to help you validate your design before moving into low-volume production.





How to Work With Us
Upload a CAD File
To start, simply select a manufacturingprocess and upload a 3D CAD file.
Get Quote with DFM
Within a few hours we’ll send you designfor manufacturability(DFM) analysis andreal-time pricing.
Manufacturing Begins
Once you review your quote and placeyour order, we’ll start the manufacturingprocess. We also offer finishing options.
Parts are Shipped!
Our digital manufacturing process allowsus to produce parts in as fast as 1 day.
Advantages of Low-Volume Manufacturing
Want to turn your product from concept to reality quickly? Small-batch production offers not only speed and flexibility but also a host of unexpected advantages. Here are the key benefits that help your innovation reach the market faster and more reliably:
Quality Assurance
| Driven by excellence, we embed quality into every detail—from advanced tools to rigorous standards. We ensure consistent, outstanding quality. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
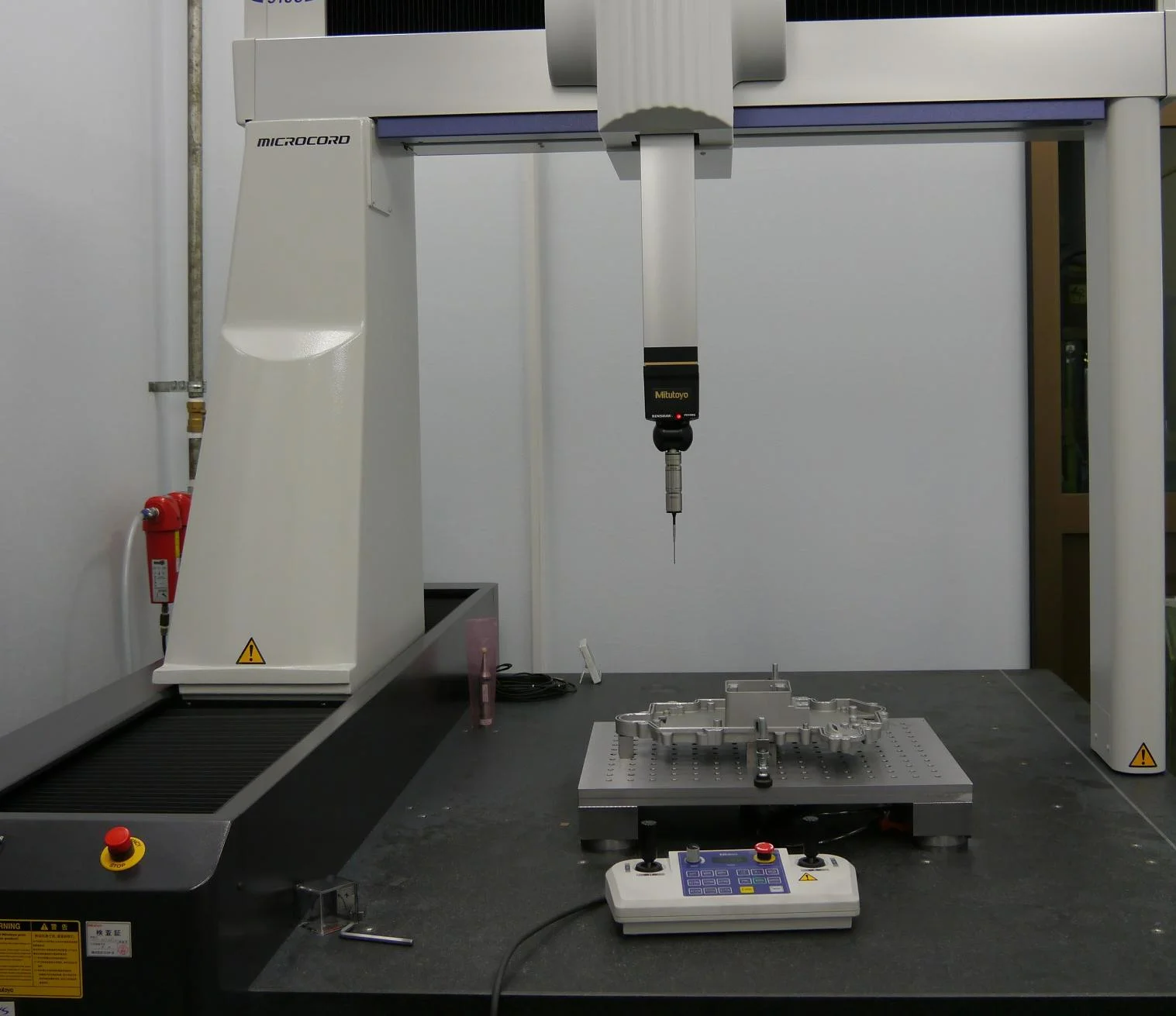
| 1 | Advanced Inspection Equipment | ||||
| We employ professional inspection equipment for precise measurement and validation. A spectrometer analyzes metal composition, a 2.5D measuring instrument verifies detailed features, a coordinate measuring machine (CMM) inspects complex three-dimensional structures, and height gauges ensure the accuracy of fundamental dimensions. | |||||
| 2 | Strict quality management system | ||||
| From first article inspection to in-process checks and final pre-shipment testing, every stage is governed by a rigorous management system to ensure consistent quality. | |||||
| IQC(Incoming Quality Control) | FAI (First Article Inspection) | ||||
| IPQC(In-Process Quality Control) | CMM inspection report | ||||
| FQC(Final Quality Control) | DIR(Dimensional Inspection Report ) | ||||
| OQC(Outgoing Quality Control) | CAR(Corrective and Preventive Action Report) | ||||
| Material Certificates | ISO 9001 | ||||
What Is Low-Volume Manufacturing

1 to 1000+
Small-Batch Production – Quality and Flexibility Combined
Wondering if small-batch production is right for your needs? The concept is simple, yet the service is highly specialized: it delivers parts in small quantities with the same quality as large-scale production. Depending on the manufacturing process, small-batch production typically handles 100,000 units or fewer, providing an efficient, flexible, and reliable solution for your product development.
Time and cost savings
Although large-scale production remains the best choice for meeting high-volume demands, small-batch production is becoming increasingly popular across industries. Why is that? Small-batch production allows clients to invest less time and money in molds and materials while bringing products to market faster. Additionally, it enables a quicker response to short product life cycles, effectively serving as a critical bridge between prototyping and full-scale manufacturing.

Low-volume-manufacturing Materials
Metal
Inconel
Inconel Superalloy Materials Inconel alloys are a family of high-performance nickel-chromium superalloys known for their exceptional strength, oxidation resistance, and high-temperature stability. These alloys are widely used in extreme environments where components are subjected to high temperatures, pressure, or mechanical loads.
Magnesium
Magnesium & Magnesium Alloy Materials Magnesium (Mg) and its alloys are among the lightest structural metals available, offering exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, good thermal conductivity, and beneficial vibration-damping properties. These materials are increasingly attractive for advanced engineering uses such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics applications where weight reduction is critical.
Titanium
Titanium Titanium is a lightweight yet high-strength metal known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and outstanding biocompatibility. It maintains stable mechanical properties across high and low temperatures and features a low thermal expansion coefficient, making it ideal for demanding applications. Thanks to these superior properties, titanium and titanium alloys are widely used
Steel Mild Low Carbon
Low-Carbon (Mild) Steel Material Low-carbon steel is a type of carbon steel with low carbon content, typically referring to steel materials with a carbon content ranging from 0.02% to 0.30%. Due to its low carbon content, it is also known as “mild steel.” Its performance characteristics are particularly notable: compared to medium-carbon steel and high-carbon
Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel Material & Alloys Stainless steel is a family of corrosion-resistant iron alloys developed to withstand oxidation, corrosion, and wear. Thanks to its excellent durability, mechanical strength, and versatile formability, stainless steel is widely used across industries requiring long-term performance—even in harsh or aggressive environments. Its favorable operational and welding properties can fully meet
Copper
Copper Material & Copper Alloys Copper is a metal that is corrosion-resistant, extremely electrically conductive, and highly ductile. Its glossy orange-red appearance is instantly recognizable, and the metal remains aesthetically appealing even during its natural oxidation process—where environmental reactions form a bluish-green coating known as patina. However, it should be noted that copper’s weldability is
Brass
Brass Material & Brass Alloys Explore HorizonRP’s brass materials—offering excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and attractive appearance. Ideal for hardware, plumbing, decorative, electrical, and industrial applications. Brass is an alloy composed of copper and zinc, with a golden color and excellent weather and corrosion resistance. Its tensile strength is comparable to that of mild steel. In
Aluminum
Aluminum Material & Aluminum Alloys Aluminum is highly favored in CNC machining due to its low density, excellent mechanical properties, superior thermal and electrical conductivity, and outstanding corrosion resistance. Among aluminum alloys, 6061-T651, 7075-T651, and 2024-T351 are widely used for their ideal balance of strength, machinability, and cost.
Plastic
TPU
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) for CNC Machining HorizonRP offers high-quality Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) material, known for its flexibility, durability, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals. Ideal for CNC machining applications, TPU is widely used across various industries, including automotive, medical, and consumer electronics.
PC+ABS
PC/ABS (Polycarbonate‑ABS Blend) Plastic Material PC+ABS is a blend-modified material that combines the advantages of both materials. It not only inherits the high impact resistance of PC but also the material strength of ABS, while improving its heat resistance. It is often used in electronic product casings, automotive interiors, consumer products, and more.
CPVC
CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) Plastic Material CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) is a modified form of PVC, with enhanced thermal stability, mechanical properties, and chemical resistance. These upgraded characteristics make CPVC an excellent choice for applications in high-temperature and corrosive environments where ordinary PVC would fail.
PC+GF
PC+GF(Glass‑Fiber Reinforced Polycarbonate) Material PC+GF (polycarbonate + glass fiber reinforced composite material) is a reinforced engineering plastic made by adding glass fiber (abbreviated as GF) to a polycarbonate (PC) matrix. The addition of glass fiber can significantly improve the mechanical properties and stability of pure PC while retaining some of PC’s excellent inherent properties, making
PEI
PEI (Polyetherimide) Engineering Material PEI (polyetherimide) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for excellent heat resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical stability. It is widely used in demanding applications across aerospace, electronics, medical, and industrial fields.
LDPE
LDPE Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is lighter than water, soft and tough, with excellent acid and alkali resistance as well as electrical insulation properties. It is widely used in fields such as packaging, agriculture, electronics, and daily necessities.
PP
PP Polypropylene (PP) is a well-balanced thermoplastic characterized by lightweight material, excellent chemical resistance, and good flexibility. Owing to these properties, it finds wide application in fields such as packaging, household appliances, automotive, daily necessities, and medical devices.
PET
PET PET (polyethylene terephthalate) is a common thermoplastic polyester with excellent mechanical properties and strong chemical resistance. It also offers glass-like transparency and luster, with a high light transmittance of about 88–92%, and is widely used in beverage bottles, food packaging, and engineering plastics.
PVC
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Plastic Material Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer material characterized by excellent mechanical properties, outstanding corrosion resistance, and superior electrical insulation performance. By incorporating various additives, it can be tailored to meet customized requirements. Owing to its unique combination of properties, PVC finds extensive applications in fields such as
PC
PC (Polycarbonate) Engineering Material PC (polycarbonate) is a versatile engineering plastic known for its high impact resistance, optical transparency, and good thermal stability. It combines toughness, heat resistance, and aesthetic clarity, making it suitable for a wide array of applications.
PMMA (Acrylic)
PMMA (Acrylic) Engineering Material Acrylic (also known as polymethyl methacrylate, PMMA) boasts not only excellent optical performance but also outstanding UV resistance. With a light transmittance of up to 92%—comparable to glass—it has become a popular material in scenarios ranging from neon signs in shopping malls and display case panels in museums to precision optical
PEEK
PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) Engineering Material PEEK (polyetheretherketone) is a premium thermoplastic widely recognized for its exceptional thermal stability, mechanical strength, chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and in many cases biocompatibility and electrical insulation. It is used in extreme environments like aerospace, medical implants, electronics, and semiconductor industries.
Nylon
Nylon (Polyamide) Engineering Material Nylon (polyamide) is a versatile engineering thermoplastic known for its high strength, excellent wear resistance, good chemical stability, and toughness. It is widely used across industries for gears, bearings, bushings, automotive components, industrial parts, and more. Its ease of machining, coupled with its chemical resistance, also makes it suitable for applications
POM
POM (Polyoxymethylene / Acetal) Engineering Material POM (polyoxymethylene), also known as acetal, is a high‑performance engineering thermoplastic valued for its rigidity, low friction, excellent wear resistance, and good dimensional stability. It is often used in precision mechanical parts that require durable, low‑maintenance performance.
HIPS
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) Material HIPS, or High Impact Polystyrene, is a modified polystyrene polymer enhanced with rubber modifiers (usually polybutadiene) to improve toughness and durability. The result is a rigid yet impact-resistant thermoplastic that retains good processability, making it popular in prototyping, manufacturing, and consumer products. HIPS combines the stiffness of polystyrene with improved
HDPE
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) Material High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with high strength-to-density ratio, known for durability, chemical resistance, and ease of processing. As a semi-crystalline plastic, it offers excellent impact performance, low moisture uptake, and good machinability — making it a popular choice in industrial, chemical, packaging, and structural applications. It is great
ABS
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) Material ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a widely used engineering thermoplastic known for its excellent balance of strength, toughness, and processability. Because it combines rigidity from acrylonitrile and styrene with impact resistance from butadiene, ABS is commonly used in consumer products, enclosures, housings, and structural components.
Surface Finish and Post-Processing Options

As machined
The machined or deburring finish is the standard finish where unwanted attach chips are removed with deburring tools, and sharp edges are chamfered to smooth the surface (3.2 μm).

Bead Blasted
Bead blasting produces a matte texture, removing all the marks of machining tools. It applies to ABS, Aluminum, Brass, Stainless Steel, and Steel parts.

Anodizing
Anodizing involves adding an aluminum oxide coating to aluminum and its alloys. The layers, which come in various colors, increase strength and shield the surface from corrosion.

Alodine
Provides excellent corrosion resistance property to the aluminum parts with greenish-gold color. It is the low-cost and quick surface finishing approach.
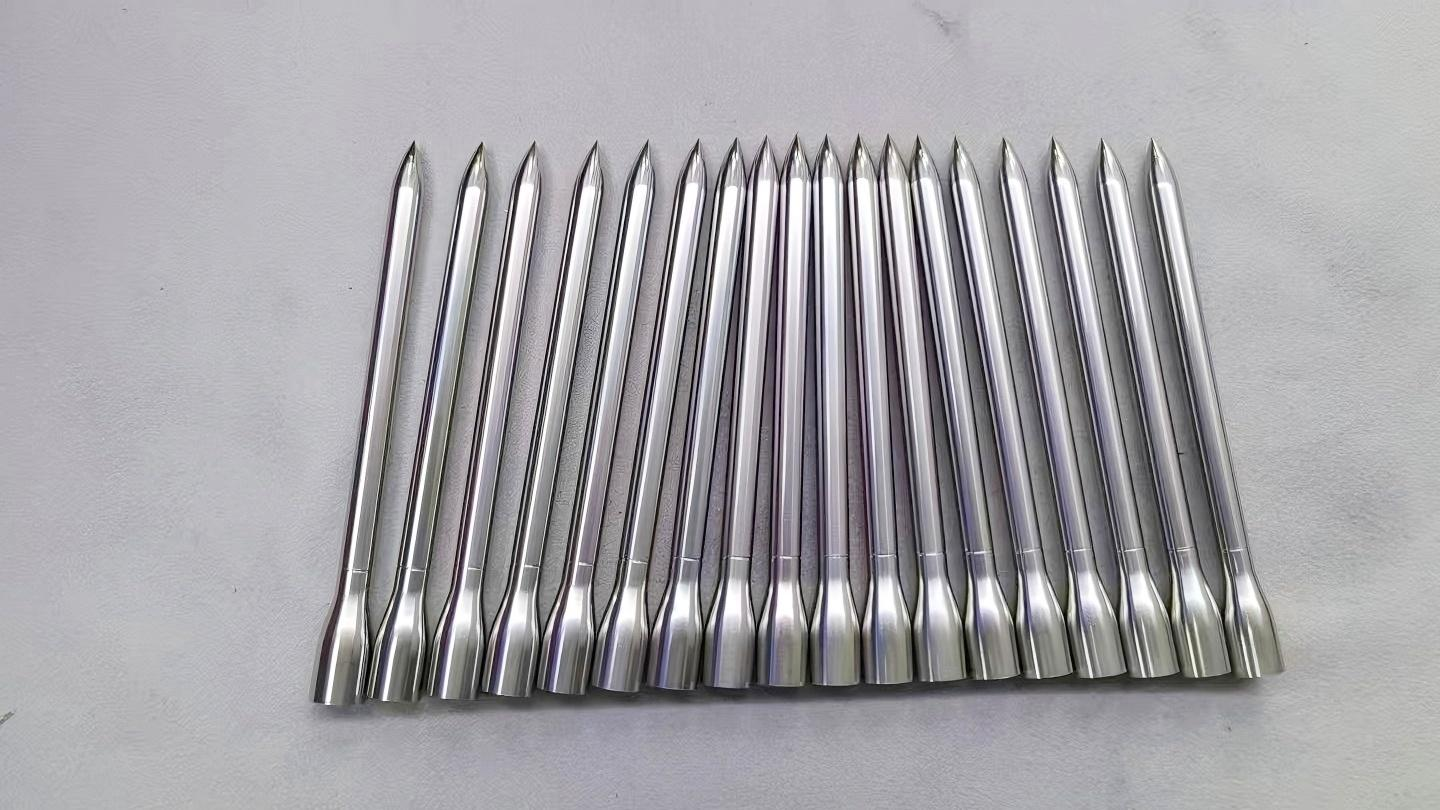

Polishing
Physical rubbing of a metal surface to create a shiny surface is called a polishing surface finish. It increases the reflectivity and does not affect the dimensional stability of parts.
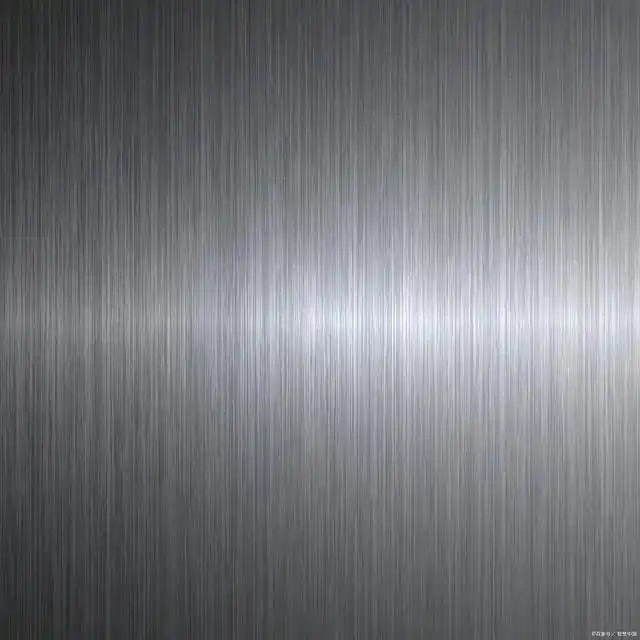

Brushing
Brushing is achieved by applying an abrasive brush to the metal surface, which produces a unidirectional satin finish. And it is not recommended for highly corrosive materials.

Sanding
Provides a random, non-linear texture with a shiny, high gloss finish. However, it might be unable to create sharp corners and pockets

Black-Oxide
Black oxide finish reduces surface reflectivity and offers mild corrosion protection. It involves adding a thin layer of magnetite to the surface.
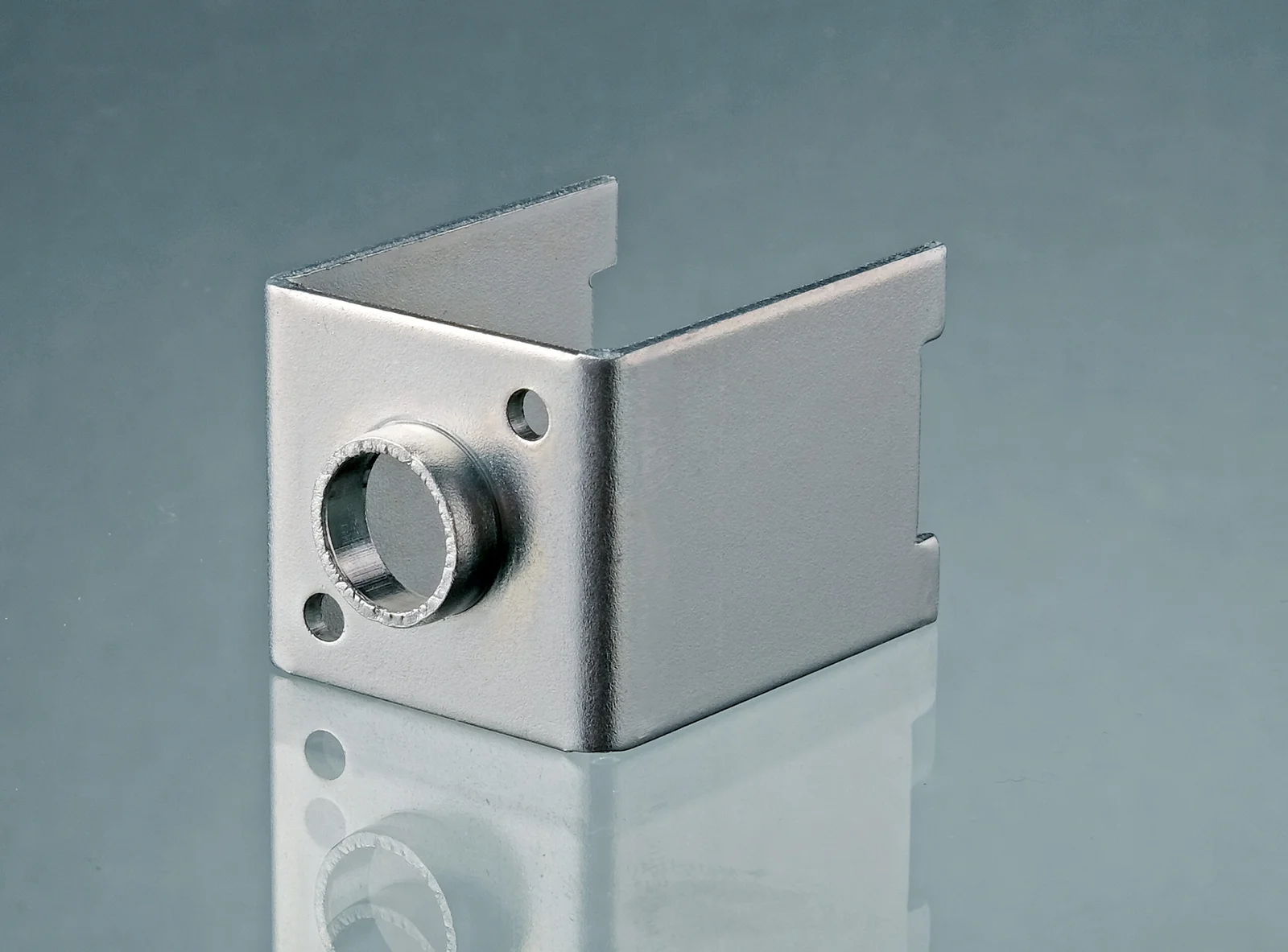

Electroplating
Electroplating increases the hardness of the steel &aluminum parts. It offers excellent corrosion, wears, and abrasion resistance.
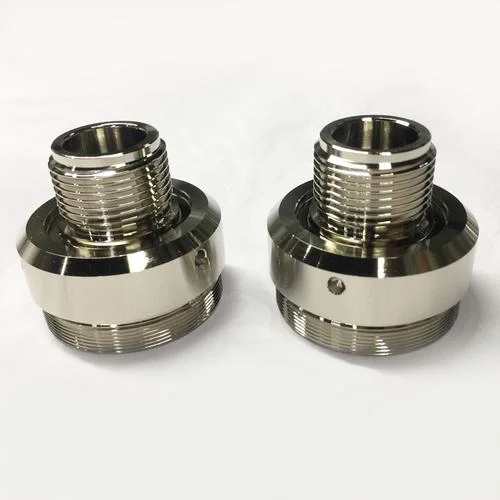

Electroless Nickel Plating
A thin layer of Nickel is created on the surface from a nickel-containing solution without electrolysis. Electro-less nickel plating provides a shiny appearance, excellent hardness, abrasive, wear, and corrosion-resistance to the substrate material.
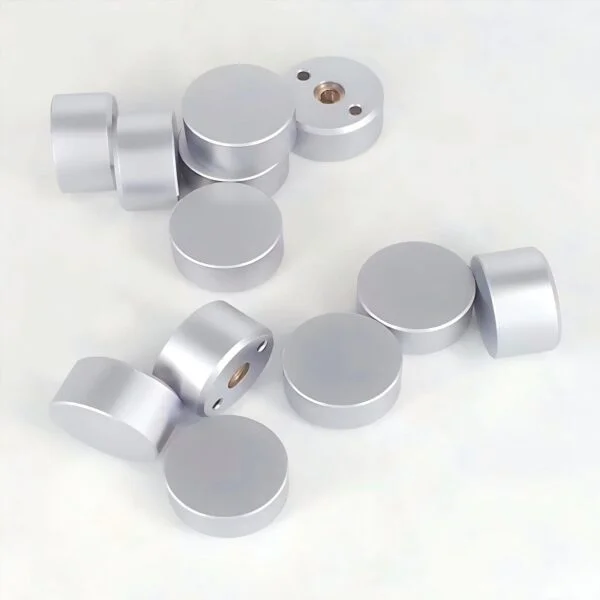

Chrome Plating
Chrome plating is widely used in various industries, which not only enhances the beautiful appearance of the product, but also improves the performance of the product, such as corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, abrasion resistance, hardness, etc.
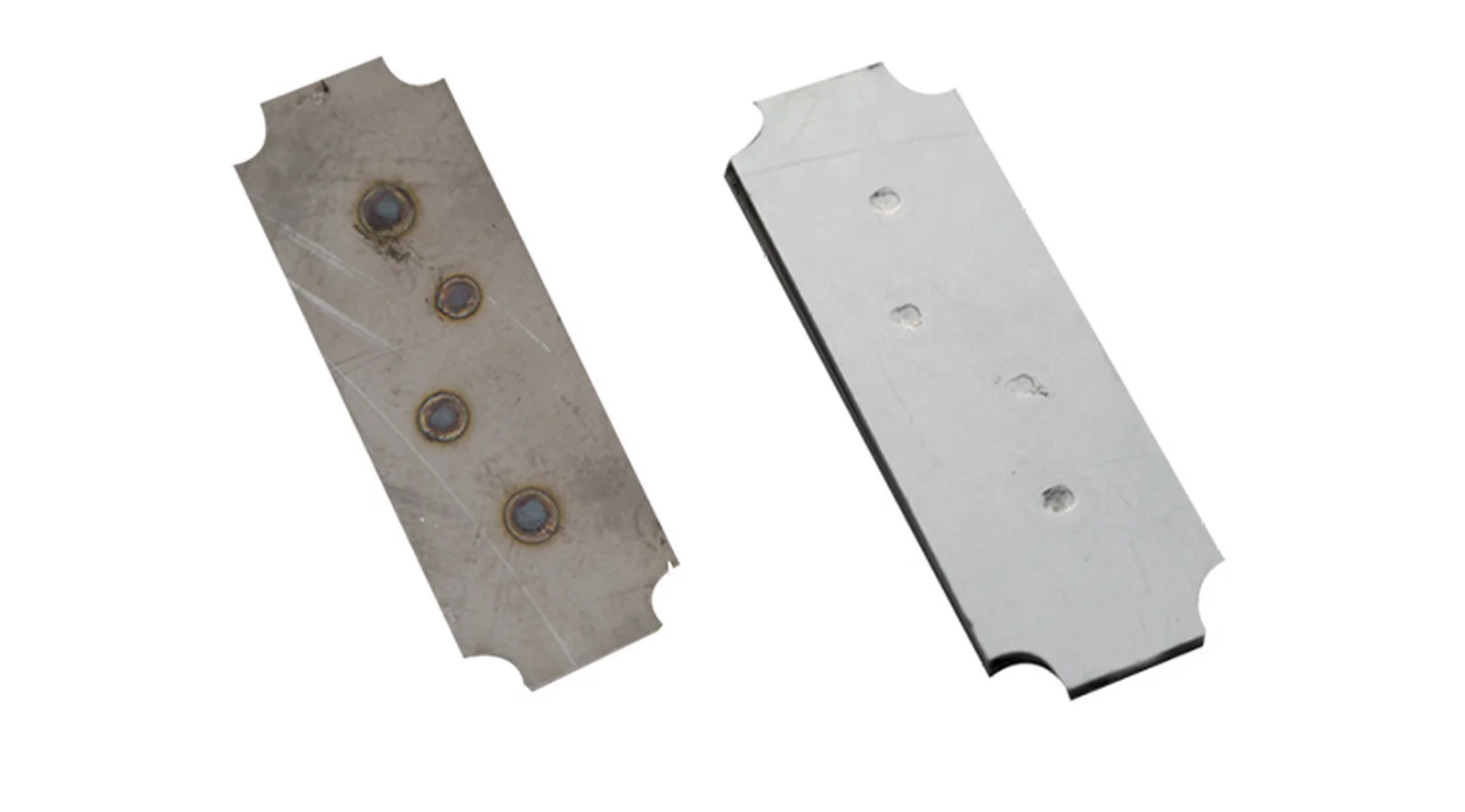

Passivation
Enhance the appearance and functionality of the parts. After Passivation, parts of Steel and its alloys become super resistive from corrosion.