Compare 3D Printing Materials
Explore and compare 3D printing materials to find the best fit for your project. From durable plastics to flexible resins, our guide highlights key properties like strength, flexibility, and surface finish, helping you choose the right material for prototyping, production, or custom parts.
PETG
Process: FDM
Durability, Strength
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) is a 3D printing material that combines strength and toughness, offering the advantages of PLA’s ease of printing and ABS’s durability. It has excellent impact resistance and chemical stability, along with good transparency and a smooth surface finish. PETG has high-temperature resistance, making it ideal for producing functional parts, mechanical components, and durable prototypes. During printing, it experiences minimal shrinkage and warping, making it a reliable choice for home, education, and industrial applications.
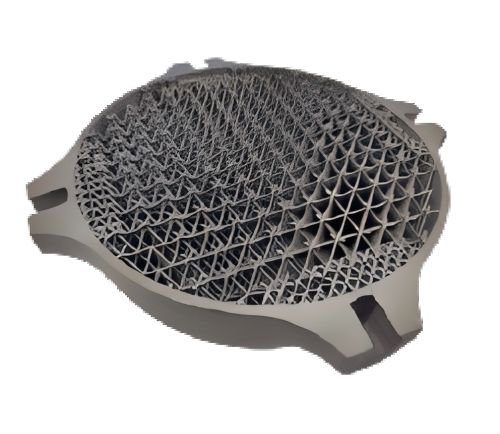
Inconel 718
Process: SLM
Fatigue Resistant, Temperature Resistance, Corrosion Resistance, Strength
Inconel 718 is known for its outstanding high-temperature strength, creep resistance, and corrosion resistance. The material can withstand operating temperatures above 700°C while maintaining excellent fatigue and fracture resistance. Through additive manufacturing, GH4169 can produce parts with complex geometries and is widely used in aerospace engines, gas turbines, high-temperature molds, and high-performance industrial components.
Disadvantages: High cost; complex heat treatment process; thin-walled structures require careful design; default surface roughness Ra10–12.Titanium
Process: SLM
Temperature Resistance, Corrosion Resistance, Strength, Lightweight
3D printed titanium alloys, represented by Ti6Al4V, feature extremely high specific strength and excellent corrosion resistance, while being lightweight and tough. They enable the creation of complex geometries and topology-optimized designs through additive manufacturing, and are widely used in aerospace, medical implants, automotive, and high-performance sports equipment. Titanium alloys also offer good high-temperature performance and biocompatibility, making them an ideal choice for manufacturing high-performance, lightweight components.
Disadvantages: Poor heat resistance (maximum 120°C); surface roughness around Ra10, with slight pits and visible layer texture.Stainless Steel 316L
Process: SLM
Durability, Corrosion Resistance, Strength
Stainless steel 316L offers excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance. It combines good mechanical strength and toughness, making it a reliable material for manufacturing acid- and corrosion-resistant components. Thanks to its outstanding corrosion resistance and its suitability as a medical- and food-grade material, it is widely used in aerospace, prototypes, tooling, and medical applications. Finished parts are typically shot-peened for surface treatment. If you require any other post-processing, please inform our customer service clearly.
Disadvantages: Poor heat resistance (maximum 120°C); surface roughness around Ra10, with slight pits and visible layer texture.Aluminum
Process: SLM
HighStrength, CorrosionResistant, Lightweight
3D printed aluminum alloys, represented by AlSi10Mg and other aluminum-silicon-magnesium alloys, combine lightweight characteristics with excellent mechanical properties. They offer an outstanding strength-to-weight ratio, good corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity, and demonstrate excellent fatigue and fracture resistance after heat treatment. The material is easy to form, weld, and machine, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and tooling applications where lightweight design and structural complexity are critical. Finished parts are typically shot-peened for surface treatment. If you require any other post-processing, please inform our customer service clearly.
Disadvantages: Poor heat resistance (maximum 120°C); surface roughness around Ra10, with slight pits and visible layer texture.