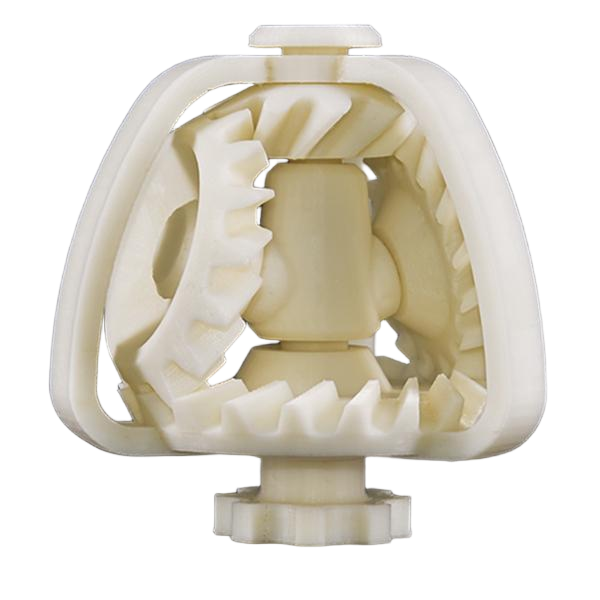
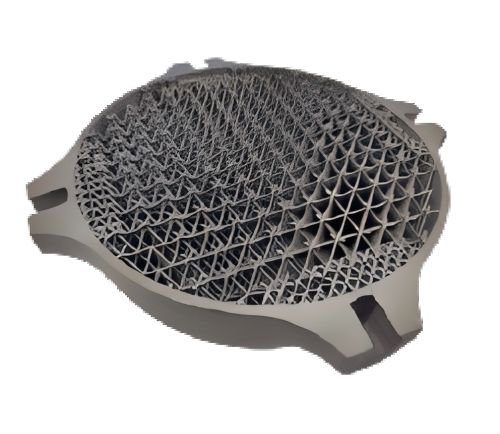
Compare 3D Printing Materials
Explore and compare 3D printing materials to find the best fit for your project. From durable plastics to flexible resins, our guide highlights key properties like strength, flexibility, and surface finish, helping you choose the right material for prototyping, production, or custom parts.
PEEK
Process:
Corrosion Resistance, Strength, Temperature Resistant
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) is a high-performance engineering plastic widely used in aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics industries. As a material that is resistant to high temperatures, chemical corrosion, and wear, PEEK offers exceptional strength and rigidity in 3D printing, making it suitable for demanding functional parts. It can withstand temperatures exceeding 250°C and maintain stable performance under high loads and extreme conditions. PEEK also has excellent electrical insulation properties and biocompatibility, making it an ideal choice for medical implants and high-end industrial components.
PETG
Process: FDM
Durability, Strength
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) is a 3D printing material that combines strength and toughness, offering the advantages of PLA’s ease of printing and ABS’s durability. It has excellent impact resistance and chemical stability, along with good transparency and a smooth surface finish. PETG has high-temperature resistance, making it ideal for producing functional parts, mechanical components, and durable prototypes. During printing, it experiences minimal shrinkage and warping, making it a reliable choice for home, education, and industrial applications.
PLA
Process: FDM
Durability, Biodegradable, RichColors, Economical
PLA is a high-quality, high-performance, and cost-effective 3D printing material, offering excellent layer adhesion and impact resistance, resulting in durable and long-lasting prints. The base series comes in up to 30 colors, ensuring uniform color consistency and stable printing quality. PLA is made from renewable plant-based resources, eco-friendly, non-toxic, and biodegradable. It is reliable, easy to use, and provides high cost-performance with a wide range of colors, making it an ideal choice for home, education, and industrial printing.
Tough Resin
Process: SLA
Durability, Strength
3D printing tough resin material is designed for printing projects that require high durability and impact resistance. It offers excellent mechanical properties, capable of withstanding high pressure and severe impact, while maintaining precise printing details. Whether creating prototypes, functional parts, or industrial applications, the tough resin provides an ideal balance—finding the sweet spot between strength and flexibility.
PC-Like Translucent
Process: SLA
Transparency, Stiffness
PC-like translucent material combines excellent translucency with high stiffness, making it an ideal choice for precision components. Through customized post-processing, functional light-transmitting effects can be achieved, delivering both aesthetic appeal and performance. With high tensile strength and modulus, this material is especially suited for creating functional prototypes that emulate injection-molded polycarbonate, meeting the dual demands of mechanical performance and visual quality for engineering prototypes and small-batch production.
PC-Like Advanced Temp
Process: SLA
Temperature Resistance, Strength, Stiffness
PC-Like Advanced High Temp is a high-temperature reinforced material with properties similar to polycarbonate, specifically designed for functional parts that require a combination of high strength, stiffness, and heat resistance. Post-curing can further increase the heat deflection temperature of the parts, enhancing their stability and reliability in high-temperature environments. It should be noted that post-curing may reduce some aspects of durability, so a balance between strength and toughness should be considered during design.
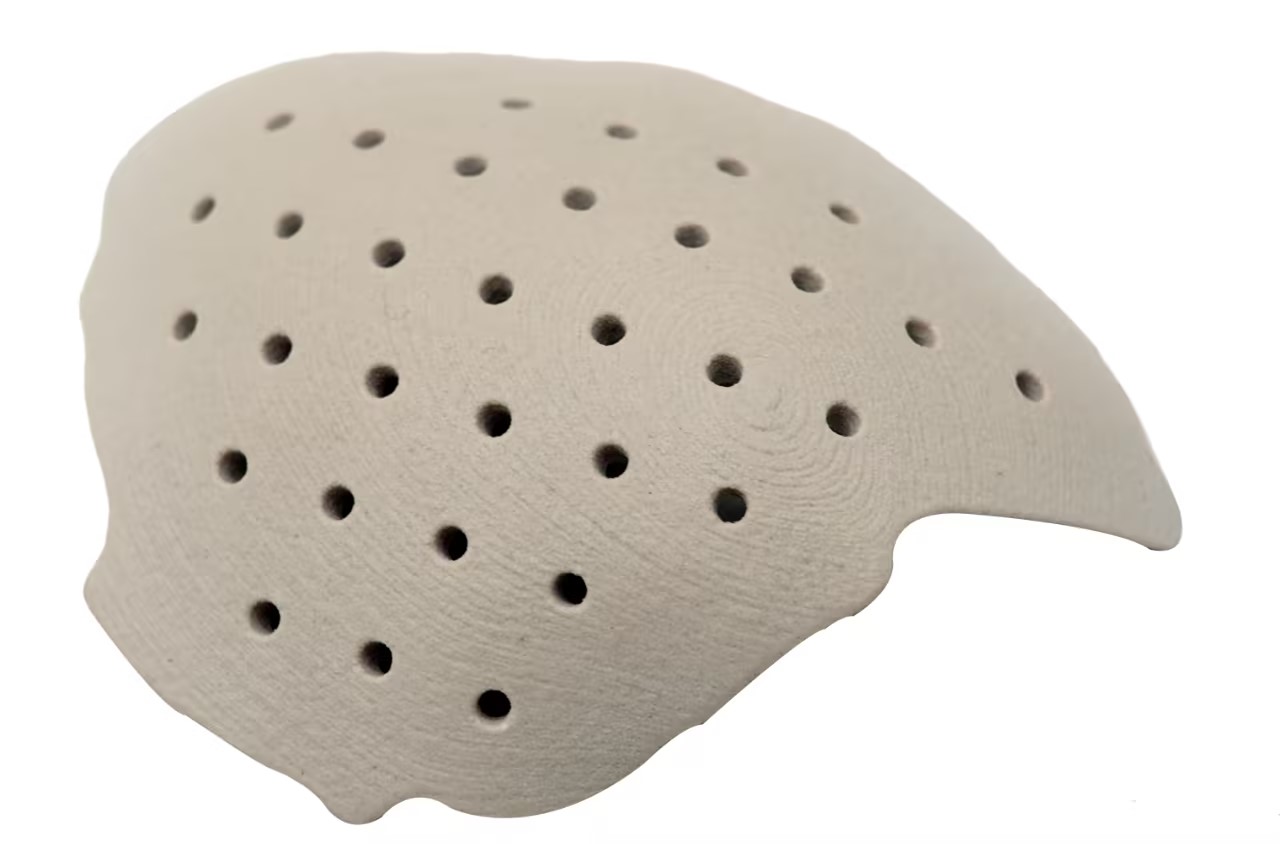
Ceramic-Like
Process: SLA
Heat Resistance, Strength, Stiffness
The high-temperature reinforced ceramic white combines exceptional heat resistance with outstanding strength and stiffness, making it an ideal choice for functional parts and high-performance prototypes. Post-curing further enhances its mechanical properties and thermal stability, providing reliable performance for complex geometries. Whether for aerospace, precision molds, electronic insulators, or laboratory equipment, this ceramic material meets the highest standards under demanding conditions, delivering solid support for innovative designs and high-performance manufacturing.
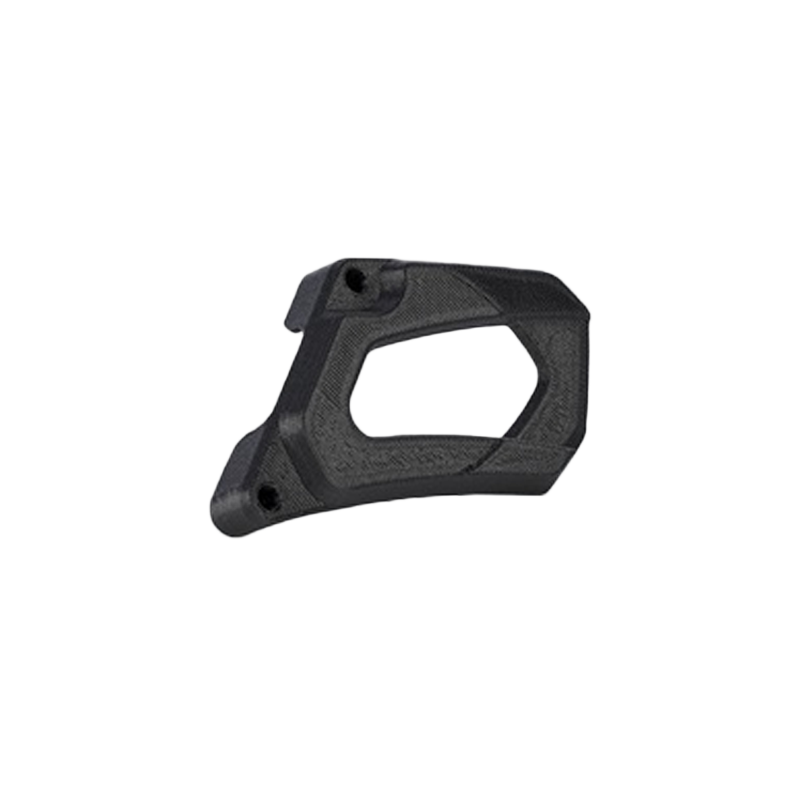
ABS-Like
Process: FDM or SLA
Moisture Resistance, Durability
ABS-like material is a durable and versatile prototyping material suitable for producing both functional and aesthetic parts. Its front surface is smooth, while the side walls and bottom have a matte finish, giving parts an appearance similar to injection-molded components. The material offers good dimensional stability, moisture resistance, and is easy to post-process, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and functional testing.It is usually available in black and white.
Inconel 718
Process: SLM
Fatigue Resistant, Temperature Resistance, Corrosion Resistance, Strength
Inconel 718 is known for its outstanding high-temperature strength, creep resistance, and corrosion resistance. The material can withstand operating temperatures above 700°C while maintaining excellent fatigue and fracture resistance. Through additive manufacturing, GH4169 can produce parts with complex geometries and is widely used in aerospace engines, gas turbines, high-temperature molds, and high-performance industrial components.
Disadvantages: High cost; complex heat treatment process; thin-walled structures require careful design; default surface roughness Ra10–12.Titanium
Process: SLM
Temperature Resistance, Corrosion Resistance, Strength, Lightweight
3D printed titanium alloys, represented by Ti6Al4V, feature extremely high specific strength and excellent corrosion resistance, while being lightweight and tough. They enable the creation of complex geometries and topology-optimized designs through additive manufacturing, and are widely used in aerospace, medical implants, automotive, and high-performance sports equipment. Titanium alloys also offer good high-temperature performance and biocompatibility, making them an ideal choice for manufacturing high-performance, lightweight components.
Disadvantages: Poor heat resistance (maximum 120°C); surface roughness around Ra10, with slight pits and visible layer texture.